1. 概述
在本教程中,我们将讨论如何合并两个最大二叉堆(Max Binary Heap)。
我们将先定义问题并举例说明,然后提出一个解决方案,并通过其实现和时间复杂度分析进行讲解。
2. 问题定义
我们有两个最大堆 H₁ 和 H₂,目标是将它们合并为一个新的最大堆 H。
最大堆的定义是:堆中每个节点的值都大于其子树中所有节点的值。我们可以用数组表示堆,数组中索引为 pos 的节点,其左子节点为 2 * pos + 1,右子节点为 2 * pos + 2。
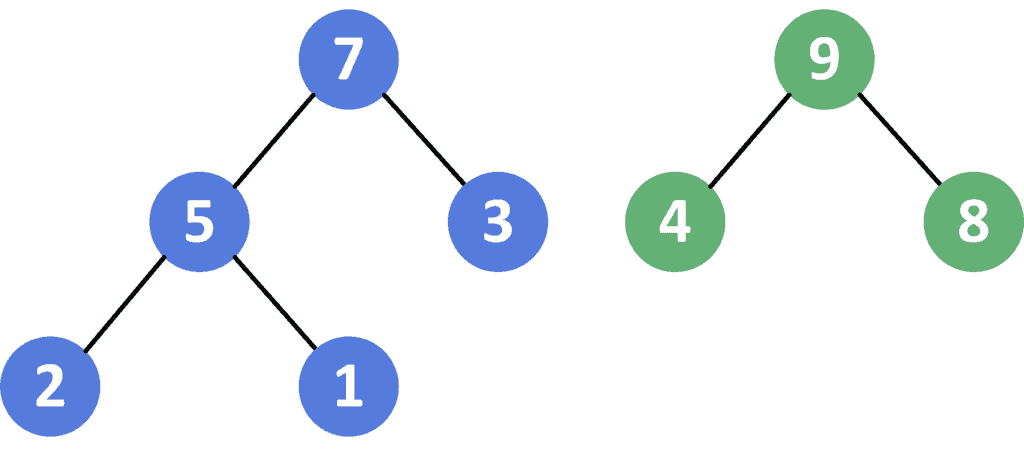
示例输入
H₁ = [7, 5, 3, 2, 1]H₂ = [9, 4, 8]
合并前的堆结构
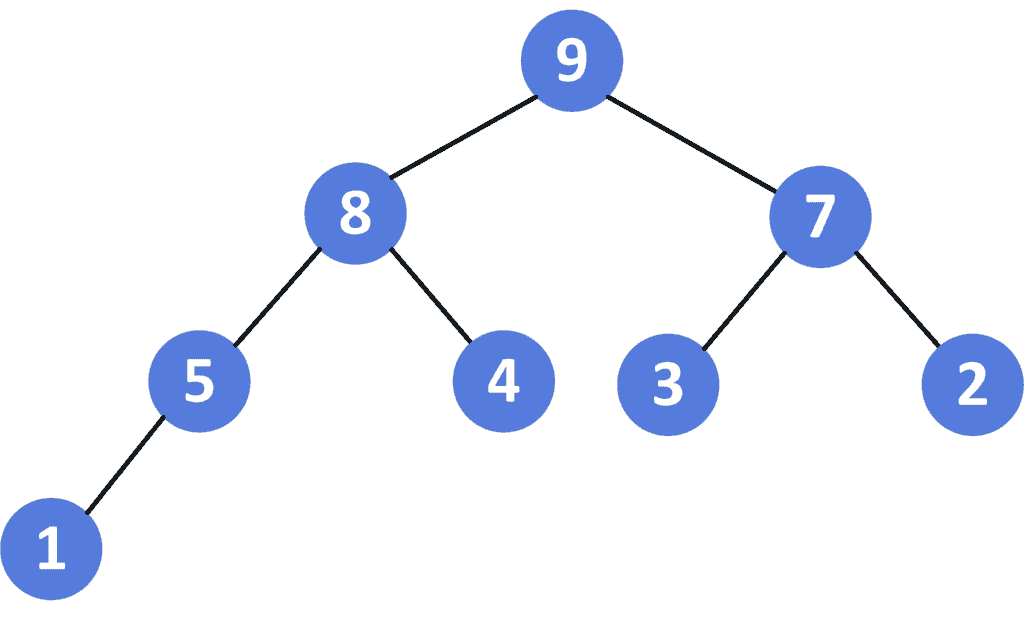
合并后的结果
H = [9, 8, 7, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
3. 解决方案
3.1. 核心思路
✅ 将两个堆的数组合并,然后基于合并后的数组重新构建最大堆。
具体步骤如下:
- 将
H₁作为初始合并后的数组; - 把
H₂中所有元素追加到H₁后; - 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,自底向上调用
maxHeapify()方法,确保整个数组满足最大堆性质。
3.2. MaxHeapify 方法
algorithm MaxHeapify(H, pos):
// INPUT
// H = The heap as an array
// pos = The position in H to start the heapify process
// OUTPUT
// Adjusts the subtree rooted at pos to satisfy the max heap property
left <- 2 * pos + 1
right <- 2 * pos + 2
max <- pos
// Check left child
if left < H.size and H[left] > H[max]:
max <- left
// Check right child
if right < H.size and H[right] > H[max]:
max <- right
// If max is not the current position, swap and continue heapifying
if max != pos:
Swap(H[max], H[pos])
MaxHeapify(H, max)
该函数的作用是:将数组中某个子树调整为最大堆结构。它递归地比较当前节点与其左右子节点,将最大值上浮,确保堆性质不变。
3.3. 合并算法实现
algorithm MergeHeaps(H1, H2):
// INPUT
// H1 = First max heap as an array
// H2 = Second max heap as an array
// OUTPUT
// A new max heap containing all the elements from H1 and H2
merged_heap <- H1
for node in H2:
add node to merged_heap
// Heapify from the last non-leaf node down to the root node
for i <- merged_heap.size - 1 down to 0:
MaxHeapify(merged_heap, i)
return merged_heap
这个函数的逻辑是:
- 将
H1复制到merged_heap; - 遍历
H2,将每个元素追加到merged_heap; - 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,逐个调用
MaxHeapify,重建最大堆; - 返回合并后的最大堆。
3.4. 时间与空间复杂度
时间复杂度:
O(N + M)
其中N是H₁的元素数量,M是H₂的元素数量。这是因为我们构建堆的时间复杂度是线性的。空间复杂度:
O(N + M)
我们创建了一个新数组来存储合并后的堆结构。
4. 小结
本文介绍了如何合并两个最大堆,并提供了一个基于数组合并后重建堆的解决方案。该方法简单高效,适用于大多数堆合并的场景。
如果你在实际项目中需要合并多个堆结构,可以考虑使用更高级的堆结构如 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci Heap),它支持 O(1) 时间复杂度的合并操作。但在大多数情况下,本文介绍的方法已经足够使用。