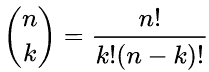1. 概述
本文将探讨几种常见的组合问题及其在 Java 中的实现方式。这类问题在日常开发中并不常见,但在算法训练或测试数据构造时非常有用✅。虽然解决方法多种多样,本文力求提供易于理解、简洁直观的解法,帮助你快速掌握核心思想。
2. 排列生成(Permutations)
排列是指对一个序列进行重排,使其顺序发生变化。数学上,一个长度为 n 的序列共有 n! 种不同排列(即阶乘):
n! = 1 × 2 × … × n
例如,序列 [1, 2, 3] 有 6 种排列:
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 3, 2]
[2, 1, 3]
[2, 3, 1]
[3, 1, 2]
[3, 2, 1]
⚠️ 阶乘增长极快:10 个元素就有 3,628,800 种排列!本文讨论的是所有元素互异的排列问题。
2.1. 算法思路
采用递归方式生成排列是一种经典做法。我们定义“状态”包含两个部分:当前排列和正在处理的元素索引。
核心逻辑如下:
- 将当前索引位置的元素与后续每一个元素(包括自己)交换
- 进入下一层递归,处理下一个索引
- 回溯时恢复交换(还原现场)
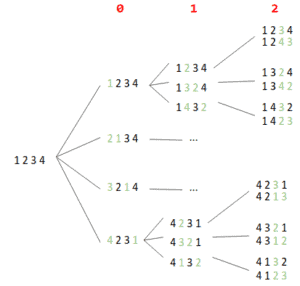
以 [1, 2, 3, 4] 为例,递归过程可表示为一棵树:
✅ 每个节点代表一个状态,红色数字为当前处理索引,绿色数字表示交换操作。最终所有排列位于最右一列。
2.2. Java 实现
private static void permutationsInternal(List<Integer> sequence, List<List<Integer>> results, int index) {
if (index == sequence.size() - 1) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>(sequence));
}
for (int i = index; i < sequence.size(); i++) {
swap(sequence, i, index);
permutationsInternal(sequence, results, index + 1);
swap(sequence, i, index); // 回溯
}
}
private static void swap(List<Integer> list, int i, int j) {
int temp = list.get(i);
list.set(i, list.get(j));
list.set(j, temp);
}
📌 关键点:
- 使用
results收集最终排列 swap后递归,再swap回去实现回溯- 复用同一个
sequence对象提升性能
封装成易用接口:
public static List<List<Integer>> generatePermutations(List<Integer> sequence) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
permutationsInternal(sequence, results, 0);
return results;
}
⚠️ 注意:该算法仅适用于元素互异的序列,否则会产生重复排列。
3. 幂集生成(Powerset)
幂集(Powerset)是指一个集合的所有子集(包括空集和自身)。例如集合 [a, b, c] 的幂集包含 8 个子集:
[]
[a]
[b]
[c]
[a, b]
[a, c]
[b, c]
[a, b, c]
数学上,n 个元素的集合有 2^n 个子集。虽然增长不如阶乘快,但依然不可小觑。
3.1. 算法思路
继续使用递归 + 回溯。状态包括:当前处理索引和累积器(accumulator)。
每个元素有两种选择:
- ✅ 加入累积器
- ❌ 不加入累积器
当索引遍历完所有元素时,累积器中的内容就是一个子集。
3.2. Java 实现
private static void powersetInternal(
List<Character> set, List<List<Character>> powerset, List<Character> accumulator, int index) {
if (index == set.size()) {
powerset.add(new ArrayList<>(accumulator));
} else {
// 选择加入当前元素
accumulator.add(set.get(index));
powersetInternal(set, powerset, accumulator, index + 1);
// 回溯:移除刚才加入的元素
accumulator.remove(accumulator.size() - 1);
// 选择不加入当前元素
powersetInternal(set, powerset, accumulator, index + 1);
}
}
📌 说明:
- 使用
List<Character>而非Set,便于按索引访问 - 每个元素处理完后有两种递归路径
- 回溯时必须移除添加的元素
提供简洁调用接口:
public static List<List<Character>> generatePowerset(List<Character> set) {
List<List<Character>> powerset = new ArrayList<>();
powersetInternal(set, powerset, new ArrayList<>(), 0);
return powerset;
}
4. 组合生成(Combinations)
k-组合是指从集合 S 中选出 k 个不同元素的子集,不考虑顺序。其数量由二项式系数决定:
例如,集合 [a, b, c] 的 2-组合有 3 个:
[a, b]
[a, c]
[b, c]
💡 实际应用:16 支球队的联赛,总共能产生 C(16,2) = 120 场不同对决。
⚠️ 注意:C(100,2)=4950,但 C(100,50) 是一个 30 位的大数!
4.1. 算法思路
类似幂集生成,但增加限制:累积器大小不能超过 k。
每个状态决策:
- ✅ 加入当前元素(如果还能加)
- ✅ 跳过当前元素
同时加入剪枝优化:如果剩余元素不足以填满 k 个,则提前终止。
4.2. Java 实现
private static void combinationsInternal(
List<Integer> inputSet, int k, List<List<Integer>> results, ArrayList<Integer> accumulator, int index) {
int needToAccumulate = k - accumulator.size();
int canAccumulate = inputSet.size() - index;
if (accumulator.size() == k) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>(accumulator));
} else if (needToAccumulate <= canAccumulate) {
// 不选当前元素
combinationsInternal(inputSet, k, results, accumulator, index + 1);
// 选当前元素
accumulator.add(inputSet.get(index));
combinationsInternal(inputSet, k, results, accumulator, index + 1);
accumulator.remove(accumulator.size() - 1);
}
}
📌 关键优化:
needToAccumulate:还需几个元素canAccumulate:还能选几个元素- 只有当
needToAccumulate <= canAccumulate时才继续递归(剪枝)
对外接口:
public static List<List<Integer>> combinations(List<Integer> inputSet, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
combinationsInternal(inputSet, k, results, new ArrayList<>(), 0);
return results;
}
5. 总结
本文介绍了三种经典组合问题的递归解法:
- ✅ 排列:全排列,元素互异,用交换+回溯
- ✅ 幂集:所有子集,每个元素二选一
- ✅ 组合:固定大小子集,带剪枝优化
这些算法虽然简单,但在生成测试用例、暴力搜索等场景下非常实用。代码已托管至 GitHub:
https://github.com/techlead-pro/tutorials/tree/master/algorithms-combinatorics