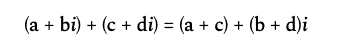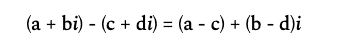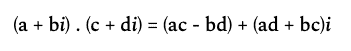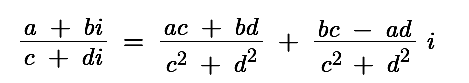1. 引言
本教程将深入探讨复数的算术运算。我们具体研究如何在 Java 中实现两个复数的加法、减法、乘法和除法操作。
2. 什么是复数?
复数由实部和虚部组合表示,通常写作 a+bi 的形式。其中 a 和 b 是实数,i 是虚数单位,等同于 -1 的平方根。在数学表达中:
- a 是复数的实部
- bi 是虚部
复数虽然对初学者可能显得抽象,但在物理学、数学等实际应用中至关重要,包括量子力学、信号处理和经济学等领域。
与实数类似,复数也能执行加、减、乘、除等算术运算。由于涉及实部与虚部的组合,复数运算会引入复杂度,但每种操作都有特定的公式确保计算准确。
3. 基础设置
在实现复数运算前,我们先构建基础代码框架。首先定义复数表示类:
public record ComplexNumber(double real, double imaginary) {
public static ComplexNumber fromString(String complexNumberStr) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(-?\\d*\\.?\\d+)?(?:([+-]?\\d*\\.?\\d+)i)?");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(complexNumberStr.replaceAll("\\s", ""));
if (matcher.matches()) {
// 提取实部和虚部
String realPartStr = matcher.group(1);
String imaginaryPartStr = matcher.group(2);
// 解析实部(若存在)
double real = (realPartStr != null) ? Double.parseDouble(realPartStr) : 0;
// 解析虚部(若存在)
double imaginary = (imaginaryPartStr != null) ? Double.parseDouble(imaginaryPartStr) : 0;
return new ComplexNumber(real, imaginary);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("无效的复数格式(" + complexNumberStr + "),支持格式为 `a+bi`");
}
}
public String toString() {
return real + "+" + imaginary + "i";
}
}
这个类使用 Java 的 record 关键字定义复数结构,包含:
real:实部imaginary:虚部
关键方法说明:
toString():将复数格式化为 a+bi 的标准形式fromString():通过正则表达式解析字符串,提取实部和虚部(支持空格和可选符号)
后续我们将在这个类中添加算术运算方法。
4. 复数加法
复数加法需分别对实部和虚部进行相加。先看数学公式:
Java 实现非常直观:
public ComplexNumber add(ComplexNumber that) {
return new ComplexNumber(real + that.real, imaginary + that.imaginary);
}
直接访问两个复数的实部和虚部,分别求和后返回新复数对象。
5. 复数减法
复数减法需分别对实部和虚部进行相减。数学公式如下:
Java 实现代码:
public ComplexNumber subtract(ComplexNumber that) {
return new ComplexNumber(real - that.real, imaginary - that.imaginary);
}
本质是分别计算实部差值和虚部差值,公式对应 (a-c)+(b-d)i。
6. 复数乘法
乘法运算比加减法复杂,需要应用分配律和虚数单位特性。数学公式:
Java 实现需注意交叉项计算:
public ComplexNumber multiply(ComplexNumber that) {
double newReal = this.real * that.real - this.imaginary * that.imaginary;
double newImaginary = this.real * that.imaginary + this.imaginary * that.real;
return new ComplexNumber(newReal, newImaginary);
}
关键点:
- 实部计算:
实部1*实部2 - 虚部1*虚部2 - 虚部计算:
实部1*虚部2 + 虚部1*实部2
7. 复数除法
除法是复数运算中最复杂的操作,需要通过有理化分母实现。数学公式:
Java 实现需处理分母为零的情况:
public ComplexNumber divide(ComplexNumber that) {
if (that.real == 0 && that.imaginary == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("禁止除以零!");
}
double c2d2 = Math.pow(that.real, 2) + Math.pow(that.imaginary, 2);
double newReal = (this.real * that.real + this.imaginary * that.imaginary) / c2d2;
double newImaginary = (this.imaginary * that.real - this.real * that.imaginary) / c2d2;
return new ComplexNumber(newReal, newImaginary);
}
实现要点:
- ✅ 先检查除数是否为 0+0i(零复数)
- 计算分母
c²+d²(避免重复计算) - 分子部分按公式展开计算
- 最终结果实部/虚部分别除以分母
8. 测试实现
为验证算术运算的正确性,需编写全面的测试用例。复数存在多种形态:
- 纯实数(如 2)
- 纯虚数(如 4i)
- 标准复数(如 3+2i)
使用 JUnit 参数化测试覆盖所有场景。以除法测试为例:
@ParameterizedTest(name = "计算 {0} ÷ {1}")
@CsvSource({
"3+2i, 1+7i, 0.34-0.38i",
"2, 4, 0.5",
"2, 4i, 0-0.5i",
"1+1i, 1+1i, 1",
"3 + 2i, 1 + 7i, 0.34-0.38i",
"0+5i, 3+0i, 0+1.6666666666666667i",
"0+0i, -2+0i, 0+0i",
"-3+2i, 1-7i, -0.34-0.38i",
"2+4i, 1, 2+4i"
})
public void givenTwoComplexNumbers_divideThemAndGetResult(String complexStr1, String complexStr2, String expectedStr) {
ComplexNumber complex1 = ComplexNumber.fromString(complexStr1);
ComplexNumber complex2 = ComplexNumber.fromString(complexStr2);
ComplexNumber expected = ComplexNumber.fromString(expectedStr);
ComplexNumber sum = complex1.divide(complex2);
Assertions.assertTrue(isSame(sum, expected));
}
public boolean isSame(ComplexNumber result, ComplexNumber expected){
return result.real() == expected.real() && result.imaginary() == expected.imaginary();
}
测试特点:
- 使用
@CsvSource覆盖 9 种典型除法场景 - 自定义
isSame()方法比较复数(避免浮点数精度问题) - 支持带空格的输入(如 "3 + 2i")
除零异常的单独测试:
@Test
public void givenAComplexNumberAsZero_handleDivideByZeroScenario() {
ComplexNumber complex1 = new ComplexNumber(1, 1);
ComplexNumber zero = new ComplexNumber(0, 0);
Exception exception = Assertions.assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class, () -> {
complex1.divide(zero);
});
Assertions.assertEquals(exception.getMessage(), "禁止除以零!");
}
9. 总结
本文完整实现了 Java 中复数的四则运算:
- ✅ 加法/减法:实部虚部分别运算
- ⚠️ 乘法:需处理虚数单位特性
- ❌ 除法:最复杂,需有理化分母并处理除零异常
通过参数化测试覆盖了多种复数形态,确保代码健壮性。完整实现代码可在 GitHub 获取。