1. 引言
本文带你深入理解最小生成树(MST)的概念,并通过 Prim 算法 手撸一个 Java 实现。这个算法在构建网络拓扑、路径优化等场景中非常实用,属于图论里的经典“必会题”。
如果你对 Dijkstra 熟悉,会发现 Prim 的思路和它惊人地相似——都是贪心 + 优先扩展最近节点。✅
2. 什么是最小生成树(MST)
最小生成树(Minimum Spanning Tree, MST) 是针对带权、无向、连通图而言的。它的目标是:保留原图的所有顶点,但选出一部分边,构成一棵树,使得所有边的权重之和最小。
⚠️ 注意几个关键词:
- 带权:边有权重,否则“最小”无意义。
- 无向:边没有方向。
- 连通:任意两点间都有路径可达。
- 树:不能有环,且边数 = 顶点数 - 1。
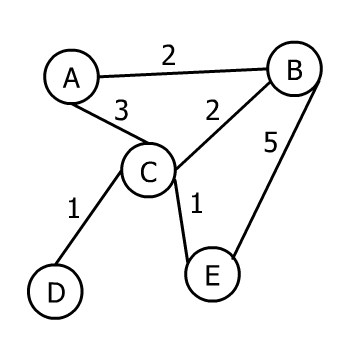
举个例子,下面是一个原始图:
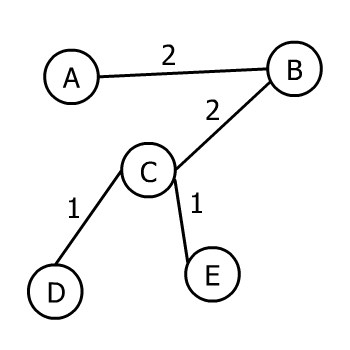
它的一个 MST 可能长这样:
✅ MST 不唯一,但所有 MST 的总权重一定相同。比如上图中,选 AB 还是 BC 都行,只要权重一样,结果总和就不变。
3. Prim 算法原理
Prim 算法的核心思想非常简单粗暴:从一个起点出发,每次选择离当前生成树最近的顶点加入,直到所有顶点都被覆盖。
它是一种贪心算法,每一步都做局部最优选择,最终得到全局最优解(在 MST 问题中成立)。
我们用下面这个图一步步演示:
步骤分解:
- 任选起点,比如选
B。 - 从
B出发,可选边:BA(2)、BC(2)、BE(5)。最小权重是 2,随便选一个,比如选A: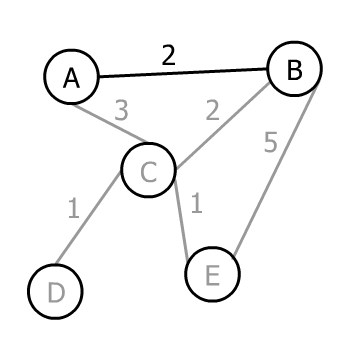
- 当前树包含
A和B,看它们连出去的未访问顶点:AC(3)、BC(2)、BE(5)。最小是BC(2),加入C: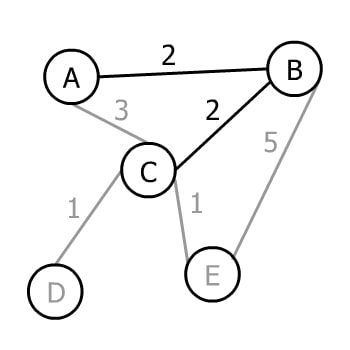
- 当前树:
A-B-C,候选边:CD(1)、CE(1)、BE(5)。最小是 1,随便选一个,比如CD,加入D: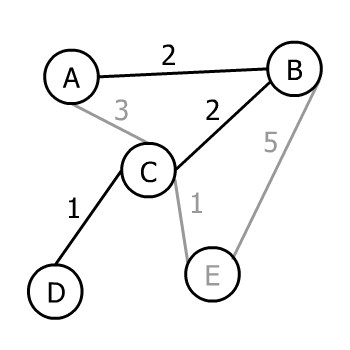
- 最后只剩
E,候选边:CE(1)、BE(5)。选最小的CE(1),加入E: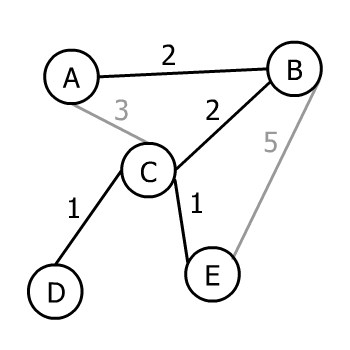
此时所有顶点已连通,算法结束。最终得到的树就是 MST。
4. Java 实现
我们从数据结构开始搭建,避免踩坑:边、顶点、主算法类。
4.1 边(Edge)类
public class Edge {
private int weight;
private boolean isIncluded = false;
public Edge(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public boolean isIncluded() {
return isIncluded;
}
public void setIncluded(boolean included) {
isIncluded = included;
}
}
weight:边的权重。isIncluded:标记该边是否已被加入 MST。
4.2 顶点(Vertex)类
public class Vertex {
private String label;
private Map<Vertex, Edge> edges = new HashMap<>();
private boolean isVisited = false;
public Vertex(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
public void addEdge(Vertex vertex, Edge edge) {
edges.put(vertex, edge);
}
public String getLabel() {
return label;
}
public boolean isVisited() {
return isVisited;
}
public void setVisited(boolean visited) {
isVisited = visited;
}
public Pair<Vertex, Edge> nextMinimum() {
Edge nextMinimum = new Edge(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Vertex nextVertex = this;
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, Edge> entry : edges.entrySet()) {
Vertex neighbor = entry.getKey();
Edge edge = entry.getValue();
if (!neighbor.isVisited() && !edge.isIncluded()) {
if (edge.getWeight() < nextMinimum.getWeight()) {
nextMinimum = edge;
nextVertex = neighbor;
}
}
}
return new Pair<>(nextVertex, nextMinimum);
}
}
edges:用Map<Vertex, Edge>存储邻接边,查找方便。nextMinimum():关键方法,从当前顶点出发,找一个未访问、未加入 MST、权重最小的邻接边和目标顶点。
💡 这里用
Pair是为了返回顶点和边两个对象。实际项目中可用SimpleEntry或自定义 DTO。
4.3 Prim 主类
public class Prim {
private List<Vertex> graph;
public Prim(List<Vertex> graph) {
this.graph = graph;
}
public void run() {
if (graph.isEmpty()) return;
// 任选一个起点,标记为已访问
graph.get(0).setVisited(true);
while (isDisconnected()) {
Edge nextMinimum = new Edge(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Vertex nextVertex = null;
// 遍历所有已访问的顶点,找全局最小边
for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
if (vertex.isVisited()) {
Pair<Vertex, Edge> candidate = vertex.nextMinimum();
if (candidate.getValue().getWeight() < nextMinimum.getWeight()) {
nextMinimum = candidate.getValue();
nextVertex = candidate.getKey();
}
}
}
// 将找到的边和顶点加入 MST
nextMinimum.setIncluded(true);
nextVertex.setVisited(true);
}
}
private boolean isDisconnected() {
for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
if (!vertex.isVisited()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 用于打印原始图
public String originalGraphToString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, Edge> entry : vertex.getEdges().entrySet()) {
sb.append(vertex.getLabel())
.append(" --- ")
.append(entry.getValue().getWeight())
.append(" --- ")
.append(entry.getKey().getLabel())
.append("\n");
}
}
return sb.toString().replaceAll("\n$", "");
}
// 用于打印 MST
public String minimumSpanningTreeToString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, Edge> entry : vertex.getEdges().entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().isIncluded()) {
sb.append(vertex.getLabel())
.append(" --- ")
.append(entry.getValue().getWeight())
.append(" --- ")
.append(entry.getKey().getLabel())
.append("\n");
}
}
}
return sb.toString().replaceAll("\n$", "");
}
// 重置打印状态(避免重复输出)
public void resetPrintHistory() {
for (Vertex vertex : graph) {
for (Edge edge : vertex.getEdges().values()) {
edge.setIncluded(false);
}
vertex.setVisited(false);
}
graph.get(0).setVisited(true);
}
}
4.4 复杂度分析
- 当前实现中,
run()中双重循环遍历顶点,nextMinimum()遍历边,总时间复杂度为 **O(V²)**。 - 如果改用优先队列(堆) 维护候选边,可以优化到 **O(E log V)**,适合稀疏图。
- 空间复杂度:O(V + E),存储图结构。
5. 测试验证
我们构造一个测试图,验证输出是否符合预期。
public static List<Vertex> createGraph() {
List<Vertex> graph = new ArrayList<>();
Vertex a = new Vertex("A");
Vertex b = new Vertex("B");
Vertex c = new Vertex("C");
Vertex d = new Vertex("D");
Vertex e = new Vertex("E");
Edge ab = new Edge(2);
Edge ac = new Edge(3);
Edge bc = new Edge(2);
Edge be = new Edge(5);
Edge ce = new Edge(1);
Edge cd = new Edge(1);
a.addEdge(b, ab);
b.addEdge(a, ab);
a.addEdge(c, ac);
c.addEdge(a, ac);
b.addEdge(c, bc);
c.addEdge(b, bc);
b.addEdge(e, be);
e.addEdge(b, be);
c.addEdge(e, ce);
e.addEdge(c, ce);
c.addEdge(d, cd);
d.addEdge(c, cd);
graph.add(a);
graph.add(b);
graph.add(c);
graph.add(d);
graph.add(e);
return graph;
}
执行测试:
Prim prim = new Prim(createGraph());
System.out.println("原始图:");
System.out.println(prim.originalGraphToString());
prim.run();
System.out.println("\nMST:");
System.out.println(prim.minimumSpanningTreeToString());
输出结果:
原始图:
A --- 2 --- B
A --- 3 --- C
B --- 2 --- C
B --- 5 --- E
C --- 1 --- D
C --- 1 --- E
MST:
A --- 2 --- B
B --- 2 --- C
C --- 1 --- D
C --- 1 --- E
✅ 完美匹配预期!总权重 = 2+2+1+1 = 6,是最小可能值。
6. 总结
- Prim 算法是求解 MST 的经典贪心算法,适合稠密图。
- 实现关键:从已访问集合出发,每次选最短边扩展。
- 基础实现 O(V²),可用优先队列优化至 O(E log V)。
- 代码中注意避免重复添加边,
isIncluded和isVisited标记要清晰。
完整代码已托管至 GitHub:https://github.com/dev-example/algorithms/tree/main/graph/prim