1. 概述
编写JUnit测试时,我们经常需要创建测试数据作为代码输入或预期输出。虽然可以在测试内或测试数据工厂类中实例化Java对象,但有时直接创建包含测试数据的文件并在测试中加载会更方便。
本文将介绍如何从文件系统加载测试数据,并展示Java Test Gadgets如何通过其Test Data Factory插件(支持JUnit 4和JUnit 5)优雅地解决这个问题。
2. 示例场景
来看一个需要文件测试数据的典型场景。
2.1. 文本转换器
假设我们正在开发一个文本处理模块,其数据模型包含:
Document包含多个ParagraphParagraph包含多个Sentence和样式Sentence包含多个Token
public class Document {
private List<Paragraph> paragraphs;
}
public class Paragraph {
public enum Style { NORMAL, HEADING };
private List<Sentence> sentences;
private Style style = Style.NORMAL;
}
public class Sentence {
private List<String> tokens;
}
我们需要实现一个转换器,处理 .txt 和 .md 格式文件:
public class Converter {
public static Document fromText(String text) {
// 待实现
}
public static Document fromMarkdown(String markdown) {
// 待实现
}
public static String fromDocument(Document doc) {
// 待实现
}
public static String toMarkdown(Document doc) {
// 待实现
}
}
测试时,可在 src/test/resources/testdata 目录存放测试文件 plain.txt:
Paragraph one starts here.
Then paragraph two follows. It has two sentences.
预期解析后的 Document 结构可存储为 twoParagraphs.json:
{
"paragraphs": [
{
"style": "NORMAL",
"sentences": [
{
"tokens": ["Paragraph", "one", "starts", "here."]
}
]
},
{
"style": "NORMAL",
"sentences": [
{
"tokens": ["Then", "paragraph", "two", "follows."]
},
{
"tokens": ["It", "has", "two", "sentences."]
}
]
}
]
}
2.2. 与本地对象对比
传统方式是在 TestDataFactory 类中硬编码测试数据:
public class TestDataFactory {
public static String twoParagraphs() {
return "Paragraph one starts here.\n" +
"Then paragraph two follows. It has two sentences.";
}
}
字符串数据尚可接受,但构建复杂对象时代码量激增:
public static Document twoParagraphsAsDocument() {
Paragraph paragraph1 = new Paragraph();
paragraph1.setStyle(Paragraph.Style.NORMAL);
Sentence sentence1 = new Sentence();
sentence1.setTokens(asList("Paragraph", "one", "starts", "here."));
paragraph1.setSentences(asList(sentence1));
Paragraph paragraph2 = new Paragraph();
paragraph2.setStyle(Paragraph.Style.NORMAL);
Sentence sentence2 = new Sentence();
sentence2.setTokens(asList("Then", "paragraph", "two", "follows."));
Sentence sentence3 = new Sentence();
sentence3.setTokens(asList("It", "has", "two", "sentences."));
paragraph2.setSentences(asList(sentence2, sentence3));
Document document = new Document();
document.setParagraphs(asList(paragraph1, paragraph2));
return document;
}
即使使用构建器模式优化,文件化测试数据仍是更优雅的方案。
2.3. 文件测试数据的核心需求
使用文件测试数据时需解决:
✅ 反序列化:将文件内容转换为目标类型
✅ 异常处理:优雅处理 IOException 等检查异常
✅ 动态重载:测试中修改数据后能重新加载
✅ 性能优化:避免不必要的重复文件读取
✅ 跨平台兼容:处理不同操作系统的路径差异
3. 原生Java实现
我们先看如何用原生Java实现文件加载。
3.1. 路径处理
使用 Paths.get() 构建跨平台路径:
Path path = Paths.get("src", "test", "resources",
"testdata", "twoParagraphs.txt");
3.2. 加载纯文本
通过 Files.lines() 读取文本文件:
public class TestDataFilesFactory {
public static String twoParagraphs() throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("src", "test", "resources",
"testdata", "twoParagraphs.txt");
try (Stream<String> file = Files.lines(path)) {
return file.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
}
}
}
⚠️ 注意:方法抛出 IOException,需在测试中处理或转换为 RuntimeException。
3.3. 加载JSON
使用 Jackson 的 ObjectMapper 处理JSON:
public static Document twoParagraphsAsDocument() throws IOException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
return objectMapper.readValue(
Paths.get("src", "test", "resources",
"testdata", "twoParagraphs.json").toFile(), Document.class);
}
3.4. 在测试中使用
@Test
void givenDocumentAndPlaintextInFiles_whenConvertToText_thenMatches() throws IOException {
Document source = TestDataFilesFactory.twoParagraphsAsDocument();
String asPlaintext = TestDataFilesFactory.twoParagraphs();
assertThat(Converter.fromDocument(source)).isEqualTo(asPlaintext);
}
3.5. 方案局限性
原生实现存在明显问题:
❌ 模板代码多:路径处理和异常处理重复
❌ 性能隐患:每次测试都重新加载不可变数据
❌ 维护成本高:文件路径变更需多处修改
理想方案应能声明式注入测试数据。
4. Test Data Factory for JUnit 4
4.1. 依赖配置
添加 Maven 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>uk.org.webcompere</groupId>
<artifactId>test-gadgets-junit4</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
4.2. 集成到测试类
通过 TestDataFieldsRule 实现字段注入:
@Rule
public TestDataFieldsRule rule = new TestDataFieldsRule(new TestDataLoader().addPath("testdata"));
使用 @TestData 注解注入数据:
- 默认加载
.json文件 - 通过参数指定文件名
@TestData
private Document twoParagraphs; // 加载 twoParagraphs.json
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private String twoParagraphsText;
测试代码变得异常简洁:
assertThat(Converter.fromDocument(twoParagraphs)).isEqualTo(twoParagraphsText);
5. Test Data Factory for JUnit 5
5.1. 依赖配置
<dependency>
<groupId>uk.org.webcompere</groupId>
<artifactId>test-gadgets-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
5.2. 集成到测试类
使用 @TestDataFactory 指定数据目录:
@TestDataFactory(path = "testdata")
class ConverterTestFactoryFieldsJUnit5UnitTest {
@TestData
private Document twoParagraphs;
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private String twoParagraphsText;
@Test
void givenDocumentAndPlaintextInFiles_whenConvertToText_thenMatches() {
assertThat(Converter.fromDocument(twoParagraphs)).isEqualTo(twoParagraphsText);
}
}
5.3. 参数注入
支持方法级参数注入:
@Test
void givenInjectedFiles_whenConvertToText_thenMatches(
@TestData("twoParagraphs.json") Document twoParagraphs,
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt") String twoParagraphsText) {
// 断言逻辑
}
6. 懒加载机制
当测试文件较多时,预加载所有数据可能影响性能。可注入 Supplier 实现懒加载:
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private Supplier<String> twoParagraphsText;
测试中调用 get() 获取数据:
assertThat(Converter.fromDocument(twoParagraphs.get()))
.isEqualTo(twoParagraphsText.get());
7. 测试数据集合
7.1. 集合定义
通过接口封装相关测试数据:
@TestDataCollection
public interface TwoParagraphsCollection {
@TestData("twoParagraphs.json")
Document twoParagraphs();
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
String twoParagraphsText();
}
注入集合接口:
@TestData
private TwoParagraphsCollection collection;
@Test
void testUsingCollection() {
assertThat(Converter.fromDocument(collection.twoParagraphs()))
.isEqualTo(collection.twoParagraphsText());
}
JUnit 5 支持参数注入:
@Test
void givenInjectedCollection_whenConvertToText_thenMatches(
@TestData TwoParagraphsCollection collection) {
// 测试逻辑
}
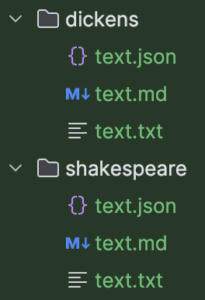
7.2. 多目录管理
定义共享接口:
@TestDataCollection
public interface AllVersions {
@TestData("text.json")
Document document();
@TestData("text.md")
String markdown();
@TestData("text.txt")
String text();
}
按目录注入:
@TestData("dickens")
private AllVersions dickens;
@TestData("shakespeare")
private AllVersions shakespeare;
8. 扩展文件格式支持
默认支持 .txt 和 .json,可扩展支持其他格式。
8.1. JUnit 4 扩展
通过 TestDataLoader 添加加载器:
@Rule
public TestDataFieldsRule rule = new TestDataFieldsRule(
new TestDataLoader()
.addLoader(".md", new TextLoader()) // 支持.md文件
.addPath("testdata"));
8.2. JUnit 5 扩展
注解方式配置:
@TestDataFactory(
loaders = { @FileTypeLoader(extension = ".md", loadedBy = TextLoader.class) },
path = "testdata")
或静态字段配置:
@TestDataFactory
class StaticLoaderUnitTest {
@Loader
private static TestDataLoader customLoader = new TestDataLoader()
.addLoader(".md", new TextLoader())
.addPath("testdata");
}
8.3. 自定义加载器
实现 ObjectLoader 接口创建自定义加载器。例如修改JSON加载器:
TestDataLoader customLoader = new TestDataLoader()
.addLoader(".json", new JsonLoader(myObjectMapper));
9. 数据复用与缓存
9.1. JUnit 4 类级别规则
使用 TestDataClassRule 共享加载器:
@ClassRule
public static TestDataClassRule classRule = new TestDataClassRule(
new TestDataLoader()
.addLoader(".md", new TextLoader())
.addPath("testdata"));
注入静态字段:
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private static String twoParagraphsTextStatic;
9.2. JUnit 5 自动处理
@TestDataFactory 自动管理静态和非静态字段注入。
9.3. 不可变数据
字符串等不可变对象自动缓存:
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private static String twoParagraphsTextStatic;
@TestData("twoParagraphs.txt")
private String twoParagraphsTextField;
// ...
assertThat(twoParagraphsTextStatic).isSameAs(twoParagraphsTextField);
9.4. 可变数据场景
测试中可能需要修改数据副本:
Document document = shakespeare.document();
document.getParagraphs().get(0).setStyle(Paragraph.Style.NORMAL);
document.getParagraphs().get(1).setStyle(Paragraph.Style.NORMAL);
assertThat(Converter.fromText(shakespeare.text())).isEqualTo(document);
9.5. 显式缓存控制
通过 immutable 参数强制缓存:
@TestData(value = "twoParagraphs.json", immutable = Immutable.IMMUTABLE)
private static Document twoParagraphsStaticImmutable;
@TestData(value = "twoParagraphs.json", immutable = Immutable.IMMUTABLE)
private Document twoParagraphsImmutable;
// ...
assertThat(twoParagraphsStaticImmutable).isSameAs(twoParagraphsImmutable);
10. 总结
本文对比了三种测试数据管理方案:
- 硬编码对象:适合简单数据,复杂场景维护困难
- 原生文件加载:灵活但模板代码多
- Test Data Factory:声明式注入,解决核心痛点
关键优势总结:
✅ 零模板代码:通过注解自动注入
✅ 多格式支持:扩展性强
✅ 性能优化:智能缓存机制
✅ 场景化组织:数据集合管理
✅ 跨版本兼容:支持JUnit 4/5
示例代码可在GitHub获取。实际项目中,建议优先使用Test Data Factory方案,避免重复造轮子。