1. 概述
本文将使用 Kotlin 编程语言实现二叉树的基本操作。如果你对 Java 实现的二叉树感兴趣,可以参考我们之前写的 Java 二叉树教程。
2. 定义
在编程中,二叉树是一种每个节点最多有两个子节点的树结构。我们通常称这两个子节点为“左子节点”和“右子节点”。
我们以整数作为节点的键值,定义一个递归的数据结构:
class Node(
var key: Int,
var left: Node? = null,
var right: Node? = null
)
每个节点包含一个整型值 key,以及可选的左子节点和右子节点。由于节点之间的链接关系,整棵树只需一个根节点就可以完整描述。
本文我们讨论的是有序二叉树(Binary Search Tree),它满足以下不变式(invariant):
- 树中不包含重复的键值
- 对于任意节点,其左子树中的所有节点键值都小于它
- 其右子树中的所有节点键值都大于它
3. 基本操作
常见的操作包括:
- 查找某个键值对应的节点
- 插入新节点
- 删除节点
- 遍历树中所有节点
3.1 查找(Lookup)
在有序二叉树中查找效率很高。如果当前节点的键值等于目标值,查找结束;如果目标值更大,则只需查找右子树;反之查找左子树:
fun find(value: Int): Node? = when {
this.key > value -> left?.find(value)
this.key < value -> right?.find(value)
else -> this
}
注意返回值可能是 null,表示未找到目标节点。
这里我们使用了 Kotlin 的 when 表达式,它比 Java 的 switch-case 更加灵活和强大。
3.2 插入(Insertion)
插入新节点时,我们需确保树中没有重复的键值。若当前节点为空,就在此插入新节点;否则根据大小关系递归地插入到左子树或右子树中:
fun insert(value: Int) {
if (value > this.key) {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = Node(value)
} else {
this.right!!.insert(value)
}
} else if (value < this.key) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = Node(value)
} else {
this.left!!.insert(value)
}
}
}
3.3 删除(Removal)
删除操作相对复杂,需要根据被删除节点的子节点数量分情况处理:
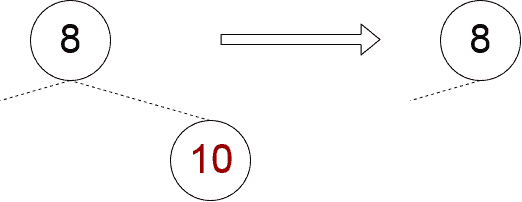
✅ 情况一:无子节点
如果目标节点是叶子节点,直接将其父节点的对应引用设为 null 即可。但注意不能删除根节点。
private fun removeNoChildNode(node: Node, parent: Node?) {
if (parent == null) {
throw IllegalStateException("Can not remove the root node without child nodes")
}
if (node == parent.left) {
parent.left = null
} else if (node == parent.right) {
parent.right = null
}
}
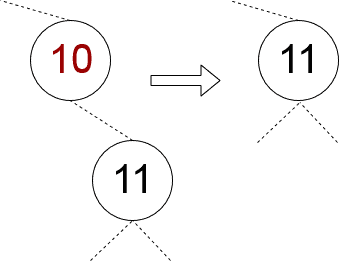
✅ 情况二:仅有一个子节点
此时只需将子节点“上提”即可,替换掉当前节点:
private fun removeSingleChildNode(parent: Node, child: Node) {
parent.key = child.key
parent.left = child.left
parent.right = child.right
}
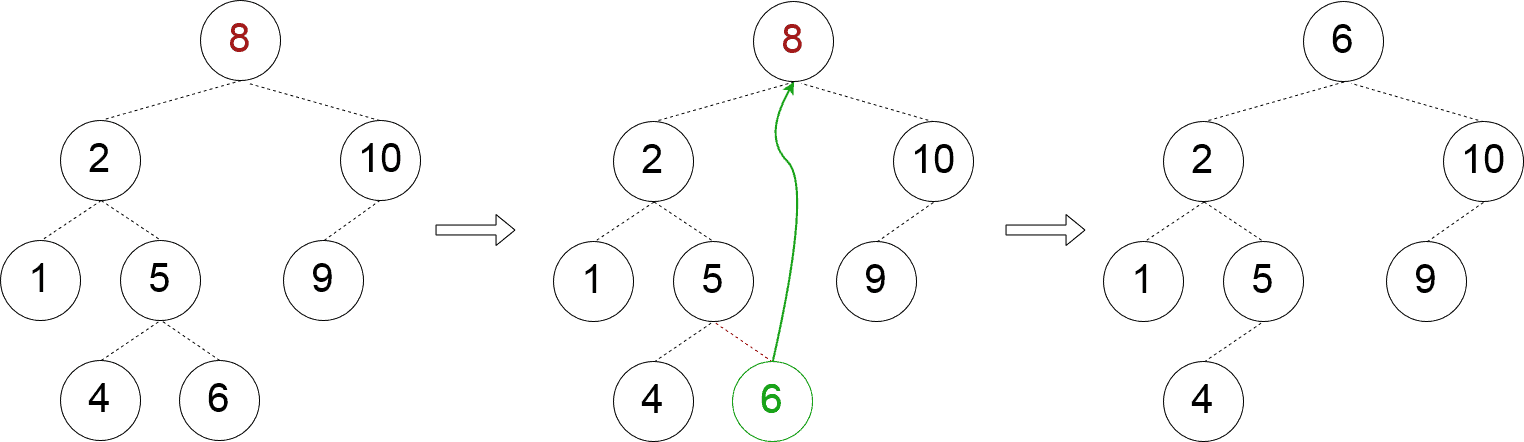
✅ 情况三:两个子节点都存在
这是最复杂的情况。我们需要找到一个合适的替代节点,通常选择左子树中最大的节点或右子树中最小的节点。
private fun removeTwoChildNode(node: Node) {
val leftChild = node.left!!
leftChild.right?.let {
val maxParent = findParentOfMaxChild(leftChild)
maxParent.right?.let {
node.key = it.key
maxParent.right = null
} ?: throw IllegalStateException("Node with max child must have the right child!")
} ?: run {
node.key = leftChild.key
node.left = leftChild.left
}
}
3.4 遍历(Traversal)
常见的遍历方式有:
- 前序遍历(Pre-order):根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
- 中序遍历(In-order):左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树
- 后序遍历(Post-order):左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点
Kotlin 中实现非常简洁:
fun visit(): Array<Int> {
val a = left?.visit() ?: emptyArray()
val b = right?.visit() ?: emptyArray()
return a + arrayOf(key) + b
}
⚠️ 注意:这种写法虽然简洁,但不是尾递归,对于深度较大的树可能会导致栈溢出。
4. 小结
本文我们用 Kotlin 实现了二叉搜索树的基本结构和操作,并演示了 Kotlin 中一些优于 Java 的语法特性,如 when、空安全操作符等。
完整代码可在 GitHub 仓库 获取。