引言
SEDA(分阶段事件驱动架构)是Matt Welsh在其博士论文中提出的一种架构风格。它的核心优势在于:
- 卓越的可扩展性
- 高并发流量处理能力
- 良好的可维护性
本教程将通过两种实现方案(Spring Integration和Apache Camel)来演示如何使用SEDA统计句子中的唯一单词数量。
SEDA架构解析
SEDA主要解决在线服务特有的非功能性需求:
- 高并发性:架构必须支持尽可能多的并发请求
- 动态内容处理:系统通常需要处理复杂业务场景,涉及多步骤请求处理
- 负载适应性:在线服务的用户流量不可预测,架构需优雅应对流量波动
为满足这些需求,SEDA将复杂服务分解为事件驱动的阶段。这些阶段通过队列间接连接,实现完全解耦。每个阶段都配备独立的扩展机制来应对负载:
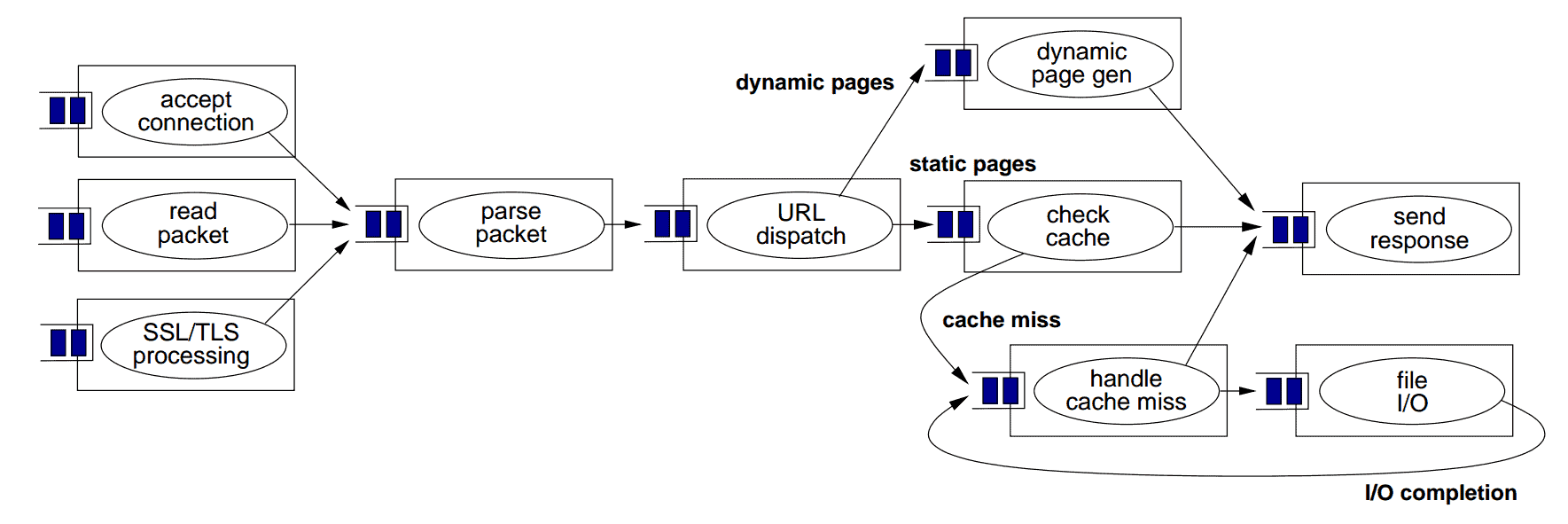
上图展示了基于SEDA的Web服务器整体结构。每个矩形代表HTTP请求的一个处理阶段,各阶段独立消费输入队列中的任务,执行处理或I/O操作后,将消息传递到下一个队列。
核心组件解析
深入理解SEDA组件,我们来看单个阶段的内部结构:
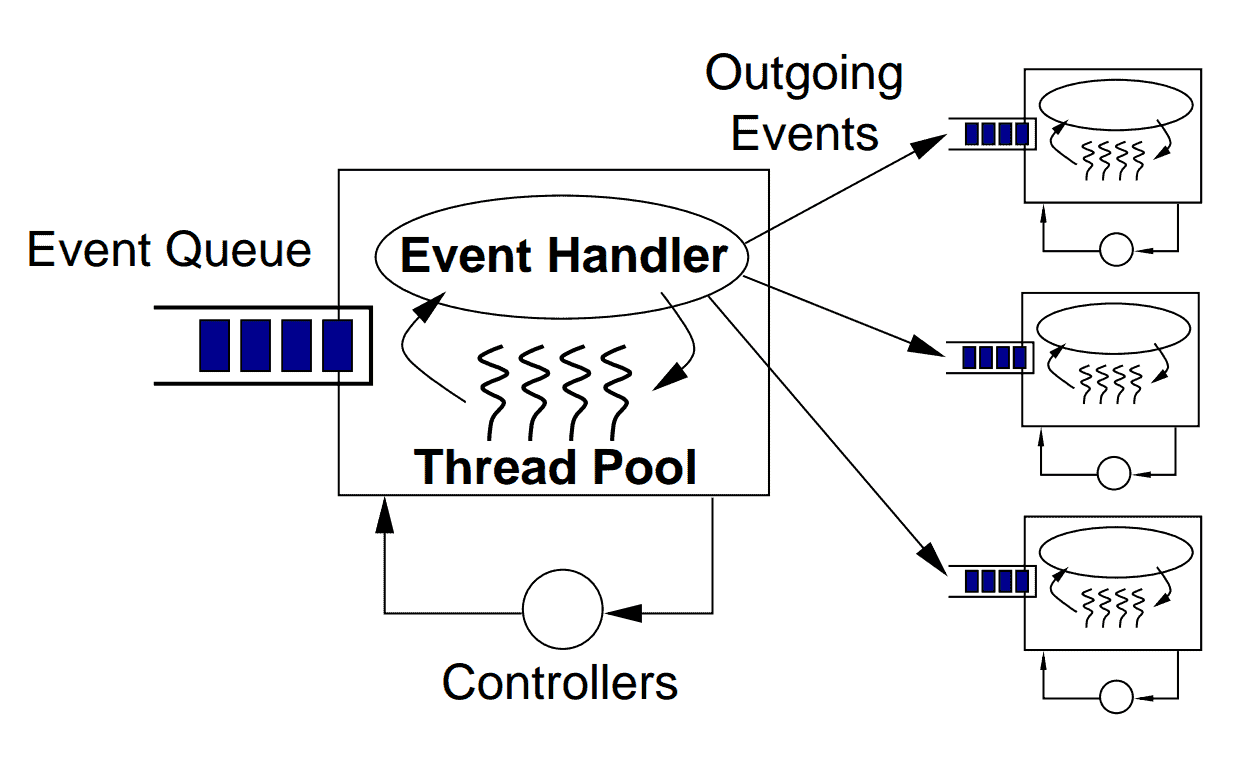
每个SEDA阶段包含以下关键组件:
- 事件:包含阶段处理所需数据的数据结构。例如HTTP服务器中的事件可能包含用户数据(请求体、头部、参数)和基础设施数据(IP地址、时间戳等)
- 事件队列:存储阶段的输入事件
- 事件处理器:阶段的核心处理逻辑。可以是简单的路由阶段(转发消息到其他队列)或复杂的数据处理阶段。支持单条或批量处理(后者适用于批量更新数据库等优化场景)
- 输出事件:根据业务流程,每个阶段可向零个或多个队列发送新事件。事件创建和发送在处理器方法中完成
- 线程池:SEDA的线程模型是本地化和定制化的。每个阶段维护独立线程池,区别于"每请求一线程"模型,用户请求由多个线程协同处理。这种设计允许针对各阶段复杂度独立调优
- 控制器:管理线程池大小、队列容量、调度等资源消耗的机制。控制器负责SEDA的弹性伸缩行为:
- 简单控制器:管理各线程池的活跃线程数
- 高级控制器:实现复杂的性能调优算法,运行时监控全局应用并调整参数
- 关键优势:将性能调优逻辑与业务逻辑解耦,提升代码可维护性
通过这些组件的协同工作,SEDA为应对高波动流量提供了健壮的解决方案。
示例问题
接下来我们将通过两种SEDA实现解决同一问题:统计给定字符串中每个单词的出现次数(不区分大小写)。
定义单词为无空格的字符序列,忽略标点等复杂情况。输出为Map结构,键为单词,值为出现次数。例如输入"My name is Hesam",输出应为:
{
"my": 1,
"name": 1,
"is": 1,
"hesam": 1
}
问题适配SEDA
从SEDA阶段角度分析问题:鉴于可扩展性是SEDA的核心目标,应设计专注于特定操作的小型阶段,特别是涉及I/O密集型任务时。小型阶段设计也有助于更精细的扩展调优。
我们的词频统计解决方案包含以下阶段:

准备好阶段设计后,下文将使用两种企业集成技术实现。各组件对应关系如下:
| SEDA组件 | Spring Integration | Apache Camel |
|---|---|---|
| 事件 | org.springframework.messaging.Message |
org.apache.camel.Exchange |
| 事件队列 | org.springframework.integration.channel |
URI定义的接口 |
| 事件处理器 | 函数式接口实例 | Camel处理器/工具类/函数 |
| 线程池 | Spring的TaskExecutor抽象 | SEDA接口内置支持 |
Spring Integration解决方案
Spring Integration基于Spring模型,支持主流的企业集成模式。其核心组件包括:
- 消息:包含头部和主体的数据结构
- 通道:在端点间传递消息的载体:
- 点对点通道:仅一个端点可消费消息
- 发布-订阅通道:多个端点可消费消息
- 端点:将消息路由到执行业务逻辑的应用组件(如转换器、路由器、服务激活器等)
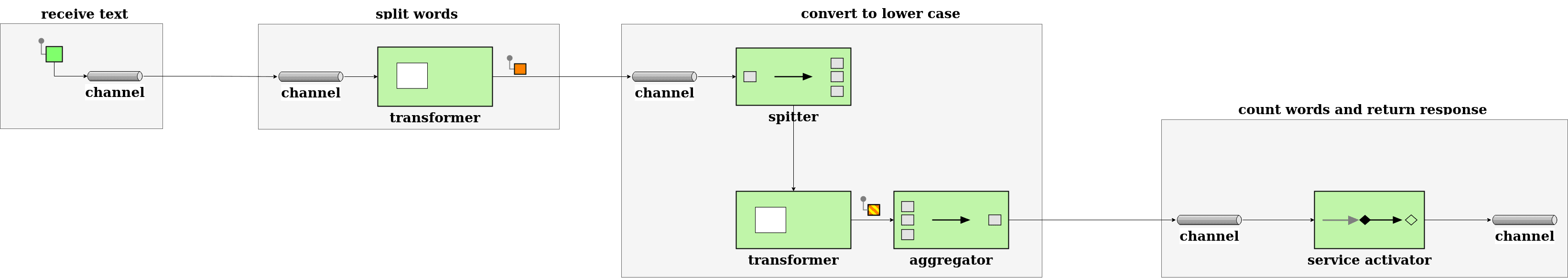
解决方案整体流程:
依赖配置
添加以下Maven依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-integration</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.integration</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-integration-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
消息网关设计
消息网关是隐藏集成流发送消息复杂度的代理:
@MessagingGateway
public interface IncomingGateway {
@Gateway(requestChannel = "receiveTextChannel", replyChannel = "returnResponseChannel")
public Map<String, Long> countWords(String input);
}
通过网关方法测试完整流程:
incomingGateway.countWords("My name is Hesam");
Spring将输入字符串包装为Message对象传入receiveTextChannel,最终从returnResponseChannel返回结果。
消息通道配置
SEDA要求通道需通过关联线程池实现可扩展性。首先创建线程池:
@Bean("receiveTextChannelThreadPool")
TaskExecutor receiveTextChannelThreadPool() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(1);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(5);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("receive-text-channel-thread-pool");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
使用线程池创建通道:
@Bean(name = "receiveTextChannel")
MessageChannel getReceiveTextChannel() {
return MessageChannels.executor("receive-text", receiveTextChannelThreadPool)
.get();
}
MessageChannels是Spring Integration的通道工厂类,这里使用executor()方法创建由线程池管理的ExecutorChannel。其他通道配置方式类似。
接收文本阶段实现
通道配置完成后,开始实现阶段:
@Bean
IntegrationFlow receiveText() {
return IntegrationFlows.from(receiveTextChannel)
.channel(splitWordsChannel)
.get();
}
IntegrationFlows是创建流程的流畅API。from()配置输入通道,channel()配置输出通道。本阶段将网关输入直接传递到splitWordsChannel。生产环境中此阶段可能更复杂(如从持久队列或网络读取消息)。
分词阶段实现
该阶段负责将输入字符串拆分为单词数组:
@Bean
IntegrationFlow splitWords() {
return IntegrationFlows.from(splitWordsChannel)
.transform(splitWordsFunction)
.channel(toLowerCaseChannel)
.get();
}
新增的transform()方法应用指定函数处理消息。splitWordsFunction实现很简单:
final Function<String, String[]> splitWordsFunction = sentence -> sentence.split(" ");
转换为小写阶段实现
将单词数组中的每个单词转换为小写:
@Bean
IntegrationFlow toLowerCase() {
return IntegrationFlows.from(toLowerCaseChannel)
.split()
.transform(toLowerCase)
.aggregate(aggregatorSpec -> aggregatorSpec.releaseStrategy(listSizeReached)
.outputProcessor(buildMessageWithListPayload))
.channel(countWordsChannel)
.get();
}
新增方法解析:
- **
split()**:使用拆分器模式将输入数组的每个元素作为独立消息发送 - **
aggregate()**:实现聚合器模式,需两个关键参数:- 释放策略:确定何时将消息合并为单条消息
- 处理器:定义如何合并消息
释放策略使用listSizeReached,在收集完所有元素时触发聚合:
final ReleaseStrategy listSizeReached = r -> r.size() == r.getSequenceSize();
处理器buildMessageWithListPayload将结果打包为List:
final MessageGroupProcessor buildMessageWithListPayload = messageGroup ->
MessageBuilder.withPayload(messageGroup.streamMessages()
.map(Message::getPayload)
.toList())
.build();
统计词频阶段实现
最后阶段将词频统计结果打包为Map:
@Bean
IntegrationFlow countWords() {
return IntegrationFlows.from(countWordsChannel)
.transform(convertArrayListToCountMap)
.channel(returnResponseChannel)
.get();
}
使用convertArrayListToCountMap函数生成词频Map:
final Function<List<String>, Map<String, Long>> convertArrayListToCountMap = list -> list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(), Collectors.counting()));
流程测试
通过网关方法测试完整流程:
public class SpringIntegrationSedaIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
TestGateway testGateway;
@Test
void givenTextWithCapitalAndSmallCaseAndWithoutDuplicateWords_whenCallingCountWordOnGateway_thenWordCountReturnedAsMap() {
Map<String, Long> actual = testGateway.countWords("My name is Hesam");
Map<String, Long> expected = new HashMap<>();
expected.put("my", 1L);
expected.put("name", 1L);
expected.put("is", 1L);
expected.put("hesam", 1L);
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}
Apache Camel解决方案
Apache Camel是强大的开源集成框架,基于四大核心概念:
- Camel上下文:整合运行时各组件
- 路由:定义消息处理路径
- 处理器:企业集成模式的现成实现
- 组件:通过JMS/HTTP/文件IO等集成外部系统的扩展点
Apache Camel提供专用SEDA组件,极大简化SEDA应用开发。
依赖配置
添加以下Maven依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-core</artifactId>
<version>3.18.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-test-junit5</artifactId>
<version>3.18.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
SEDA接口定义
接口通过URI字符串定义,SEDA接口需以"seda:"开头:
static final String receiveTextUri = "seda:receiveText?concurrentConsumers=5";
static final String splitWordsUri = "seda:splitWords?concurrentConsumers=5";
static final String toLowerCaseUri = "seda:toLowerCase?concurrentConsumers=5";
static final String countWordsUri = "seda:countWords?concurrentConsumers=5";
static final String returnResponse = "mock:result";
每个接口配置5个并发消费者,相当于每个接口最多5个线程。returnResponse为测试用的模拟接口。
扩展RouteBuilder
创建扩展RouteBuilder的类并重写configure()方法:
public class WordCountRoute extends RouteBuilder {
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
}
}
后续将在configure()方法中通过继承的便捷方法定义各阶段。
接收文本阶段实现
接收消息并直接路由到下一阶段:
from(receiveTextUri).to(splitWordsUri);
使用from()指定输入接口,to()指定输出接口。
分词阶段实现
拆分输入文本为单词数组:
from(splitWordsUri)
.transform(ExpressionBuilder.bodyExpression(s -> s.toString().split(" ")))
.to(toLowerCaseUri);
transform()方法应用函数拆分字符串为数组。
转换为小写阶段实现
需对数组中每个单词单独处理,使用split()方法拆分消息并聚合结果:
from(toLowerCaseUri)
.split(body(), new ArrayListAggregationStrategy())
.transform(ExpressionBuilder.bodyExpression(body -> body.toString().toLowerCase()))
.end()
.to(countWordsUri);
end()标记拆分过程结束。ArrayListAggregationStrategy扩展AbstractListAggregationStrategy,定义聚合消息体部分:
class ArrayListAggregationStrategy extends AbstractListAggregationStrategy<String> {
@Override
public String getValue(Exchange exchange) {
return exchange.getIn()
.getBody(String.class);
}
}
统计词频阶段实现
将数组转换为词频Map:
from(countWordsUri)
.transform(ExpressionBuilder.bodyExpression(List.class, body -> body.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(), Collectors.counting()))))
.to(returnResponse);
路由测试
测试完整路由:
public class ApacheCamelSedaIntegrationTest extends CamelTestSupport {
@Test
public void givenTextWithCapitalAndSmallCaseAndWithoutDuplicateWords_whenSendingTextToInputUri_thenWordCountReturnedAsMap()
throws InterruptedException {
Map<String, Long> expected = new HashMap<>();
expected.put("my", 1L);
expected.put("name", 1L);
expected.put("is", 1L);
expected.put("hesam", 1L);
getMockEndpoint(WordCountRoute.returnResponse).expectedBodiesReceived(expected);
template.sendBody(WordCountRoute.receiveTextUri, "My name is Hesam");
assertMockEndpointsSatisfied();
}
@Override
protected RoutesBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception {
RoutesBuilder wordCountRoute = new WordCountRoute();
return wordCountRoute;
}
}
CamelTestSupport提供丰富测试工具:getMockEndpoint()和expectedBodiesReceived()设置预期结果,template.sendBody()提交测试数据,assertMockEndpointsSatisfied()验证结果。
结论
本文深入解析了SEDA架构的组件、原理及应用场景,通过Spring Integration和Apache Camel两种技术方案实现了相同的词频统计问题。两种方案各有特点:
- Spring Integration:与Spring生态深度集成,适合已有Spring项目
- Apache Camel:提供丰富的企业集成模式实现,路由定义更直观
完整示例代码请参考GitHub仓库。