1. 概述
动态管理应用配置是许多实际场景中的关键需求。在微服务架构中,不同服务可能因扩缩容或负载变化需要实时调整配置。其他情况下,应用可能需要根据用户偏好、外部API数据或动态变化的合规要求调整行为。
传统的 application.properties 文件是静态的,修改后必须重启应用。但 Spring Boot 提供了多种强大方案,可在不重启的情况下运行时调整配置。无论是切换生产环境功能、更新数据库连接实现负载均衡,还是修改第三方集成API密钥,Spring Boot 的动态配置能力都能满足复杂场景需求。
本教程将探索多种在不修改 application.properties 的前提下动态更新 Spring Boot 属性的策略。这些方法覆盖不同需求,从非持久化的内存更新到使用外部文件的持久化修改。
示例基于 Spring Boot 3.2.4 + JDK 17,同时使用 Spring Cloud 4.1.3。不同版本可能需要微调代码。
2. 使用原型作用域 Bean
当需要动态调整特定 Bean 的属性,且不影响已创建实例或全局状态时,直接使用 @Service + @Value 注入无法满足需求(因为属性在应用上下文生命周期内是静态的)。我们可以通过 @Configuration 类中的 @Bean 方法创建可修改属性的 Bean:
@Configuration
public class CustomConfig {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public MyService myService(@Value("${custom.property:default}") String property) {
return new MyService(property);
}
}
通过 @Scope("prototype") 确保每次调用 myService(...) 都创建新实例,支持运行时不同配置。MyService 是一个简单 POJO:
public class MyService {
private final String property;
public MyService(String property) {
this.property = property;
}
public String getProperty() {
return property;
}
}
验证动态行为的测试用例:
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext context;
@Test
void whenPropertyInjected_thenServiceUsesCustomProperty() {
MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
assertEquals("default", service.getProperty());
}
@Test
void whenPropertyChanged_thenServiceUsesUpdatedProperty() {
System.setProperty("custom.property", "updated");
MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
assertEquals("updated", service.getProperty());
}
此方法提供运行时配置修改的灵活性,但变更是临时的,仅影响 CustomConfig 创建的实例。
3. 使用 Environment、MutablePropertySources 和 @RefreshScope
与上节不同,我们希望更新已实例化 Bean 的属性。此时需要结合 Spring Cloud 的 @RefreshScope 注解和 /actuator/refresh 接口。该 Actuator 会刷新所有 @RefreshScope Bean,用新配置的实例替换旧实例,实现无重启的实时更新。注意变更同样非持久化。
3.1 基础配置
在 pom.xml 添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>4.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.awaitility</groupId>
<artifactId>awaitility</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
spring-cloud-starter 和 spring-cloud-starter-config 属于 Spring Cloud 框架,spring-boot-starter-actuator 用于暴露 /actuator/refresh 接口,awaitility 是测试异步操作的实用工具。
配置 application.properties。由于本例未使用 Spring Cloud Config Server 集中管理配置,需禁用连接外部配置服务器的默认行为:
spring.cloud.config.enabled=false
若忘记此配置,应用启动时会抛出 java.lang.IllegalStateException。接着启用 Actuator 接口:
management.endpoint.refresh.enabled=true
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh
可选:记录每次 Actuator 调用:
logging.level.org.springframework.boot.actuate=DEBUG
添加测试属性:
my.custom.property=defaultValue
基础配置完成。
3.2 示例 Bean
对 Bean 使用 @RefreshScope 时,Spring Boot 不会直接实例化,而是创建代理对象作为实际 Bean 的占位符:
@RefreshScope
@Component
public class ExampleBean {
@Value("${my.custom.property}")
private String customProperty;
public String getCustomProperty() {
return customProperty;
}
}
@Value 注入 application.properties 中的属性值。代理对象拦截方法调用,当 /actuator/refresh 触发刷新事件时,代理会用新配置重新初始化 Bean。
3.3 PropertyUpdaterService 实现
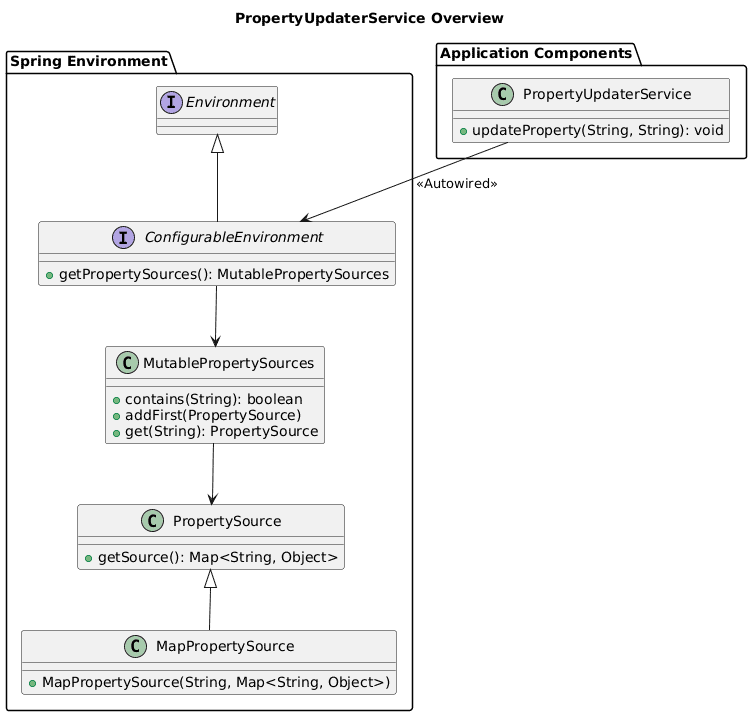
创建 PropertyUpdaterService 类运行时动态更新属性,通过管理 Spring 环境中的自定义属性源实现。关键概念:
-
Environment→ 提供属性源、配置文件和系统环境变量的访问接口 -
ConfigurableEnvironment→Environment的子接口,支持动态更新应用属性 -
MutablePropertySources→ 持有的PropertySource集合,可添加/删除/重排属性源(如系统属性、环境变量或自定义源)
UML 图展示组件关系(动态属性更新如何传播):
PropertyUpdaterService 实现:
@Service
public class PropertyUpdaterService {
private static final String DYNAMIC_PROPERTIES_SOURCE_NAME = "dynamicProperties";
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
public void updateProperty(String key, String value) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (!propertySources.contains(DYNAMIC_PROPERTIES_SOURCE_NAME)) {
Map<String, Object> dynamicProperties = new HashMap<>();
dynamicProperties.put(key, value);
propertySources.addFirst(new MapPropertySource(DYNAMIC_PROPERTIES_SOURCE_NAME, dynamicProperties));
} else {
MapPropertySource propertySource = (MapPropertySource) propertySources.get(DYNAMIC_PROPERTIES_SOURCE_NAME);
propertySource.getSource().put(key, value);
}
}
}
关键点:
-
updateProperty(...)检查是否存在dynamicProperties属性源 - 不存在则创建
MapPropertySource并设为最高优先级(addFirst) - ***
addFirst(...)确保动态属性优先级高于其他属性源** - 已存在则更新或添加属性
此服务可在运行时编程式更新任意属性。
3.4 PropertyUpdaterService 的使用策略
⚠️ 生产环境安全警告: 通过控制器直接暴露属性更新功能方便测试,但生产环境需严格防护。替代方案:
✅ 推荐安全策略:
- 定时任务 → 基于时间条件或外部数据更新属性
- 条件触发 → 响应负载变化、用户活动或外部API事件
- 受限管理工具 → 仅授权人员可访问的安全工具
- 自定义 Actuator → 提供更精细的控制和安全策略
- 事件监听器 → 响应云环境基础设施变更
内置 /actuator/refresh 仅刷新 @RefreshScope Bean,不直接更新属性。需结合 PropertyUpdaterService 先修改属性,再触发刷新。单独使用该 Actuator 无法更新/添加新属性。
选择策略应结合应用需求、配置敏感性和安全要求。
3.5 控制器手动测试
用简单控制器测试功能:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/properties")
public class PropertyController {
@Autowired
private PropertyUpdaterService propertyUpdaterService;
@Autowired
private ExampleBean exampleBean;
@PostMapping("/update")
public String updateProperty(@RequestParam String key, @RequestParam String value) {
propertyUpdaterService.updateProperty(key, value);
return "Property updated. Remember to call the actuator /actuator/refresh";
}
@GetMapping("/customProperty")
public String getCustomProperty() {
return exampleBean.getCustomProperty();
}
}
curl 手动测试流程:
$ curl "http://localhost:8080/properties/customProperty"
defaultValue
$ curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/properties/update?key=my.custom.property&value=baeldungValue"
Property updated. Remember to call the actuator /actuator/refresh
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh -H "Content-Type: application/json"
[]
$ curl "http://localhost:8080/properties/customProperty"
baeldungValue
若首次未生效(复杂应用),可重试最后命令,给 Spring Cloud 留出刷新时间。
3.6 JUnit5 自动化测试
由于属性更新是异步的(/actuator/refresh 立即返回,不等待 Bean 重构),需使用 await 处理超时。启动 Web 环境进行测试:
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PropertyUpdaterServiceUnitTest {
@Autowired
private PropertyUpdaterService propertyUpdaterService;
@Autowired
private ExampleBean exampleBean;
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Test
@Timeout(5)
public void whenUpdatingProperty_thenPropertyIsUpdatedAndRefreshed() throws InterruptedException {
// 注入新属性到测试上下文
propertyUpdaterService.updateProperty("my.custom.property", "newValue");
// 调用 Actuator 触发刷新
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<String> entity = new HttpEntity<>(null, headers);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.postForEntity("http://localhost:" + port + "/actuator/refresh", entity, String.class);
// Awaitility 等待属性更新
await().atMost(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS).until(() -> "newValue".equals(exampleBean.getCustomProperty()));
}
}
需根据实际测试需求定制属性和 Bean。
4. 使用外部配置文件
某些场景下需在应用部署包外管理配置更新,确保属性持久化变更,同时支持多应用分发。
延续前文 Spring Cloud 设置(启用 @RefreshScope 和 /actuator/refresh),使用相同控制器和 Bean。**目标是通过外部文件 external-config.properties 动态修改 ExampleBean**。文件内容:
my.custom.property=externalValue
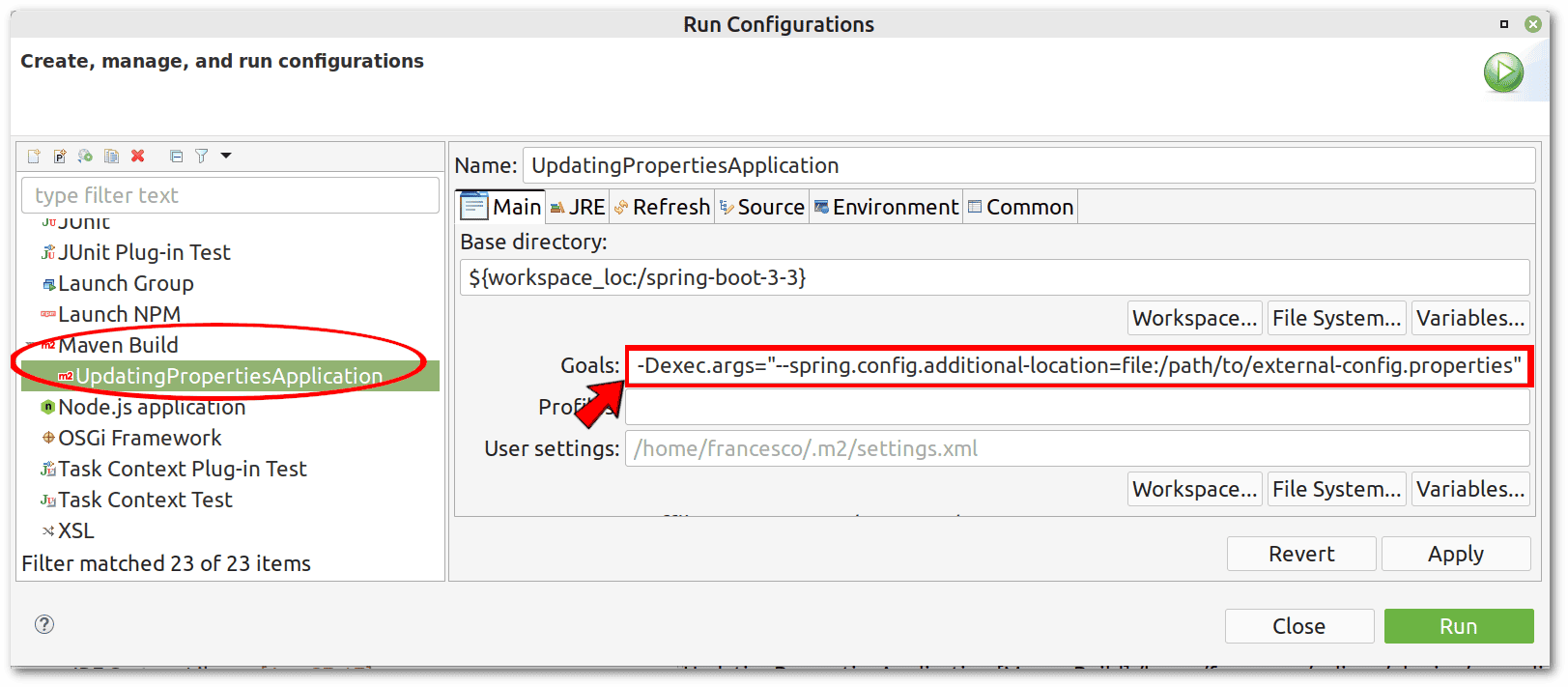
通过 --spring.config.additional-location 参数指定文件路径(Eclipse 示例):
验证外部文件加载和属性覆盖:
$ curl "http://localhost:8080/properties/customProperty"
externalValue
externalValue 已覆盖 application.properties 中的 defaultValue。修改外部文件:
my.custom.property=external-Baeldung-Value
调用 Actuator 刷新:
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh -H "Content-Type: application/json"
["my.custom.property"]
最终结果持久化生效:
$ curl "http://localhost:8080/properties/customProperty"
external-Baeldung-Value
优势:可自动化监听文件变更触发刷新。Linux/macOS 使用 fswatch:
$ fswatch -o /path/to/external-config.properties | while read f; do
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh -H "Content-Type: application/json";
done
Windows 可用 PowerShell 实现类似功能(略)。
5. 总结
本文探索了多种不修改 application.properties 而动态更新 Spring Boot 属性的方法:
- 原型作用域 Bean:通过
@Scope("prototype")实现实例级配置隔离,适合非持久化临时变更 - Spring Cloud 刷新机制:结合
@RefreshScope和/actuator/refresh实现实时 Bean 重构 - 外部配置文件:支持持久化变更和跨应用分发,适合生产环境
关键点对比:
| 方法 | 持久性 | 影响范围 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原型作用域 Bean | ❌ | 新实例 | 临时测试/隔离配置 |
@RefreshScope |
❌ | 标记 Bean | 开发环境动态调试 |
| 外部配置文件 | ✅ | 全局应用 | 生产环境集中配置管理 |
**完整源码见 GitHub 仓库**。