1. 概述
本教程将介绍如何使用Spring Cloud Function(SCF)框架开发可部署到Microsoft Azure Functions的Java应用。
我们将探讨核心概念、开发示例应用、部署到Azure Functions服务,最后进行测试验证。
2. 核心概念
Azure Functions提供无服务器环境,让我们无需管理基础设施即可部署应用。支持Java、Python、C#等多种语言,通过对应SDK框架实现。应用可响应Azure服务(如Blob存储、表存储、Cosmos DB、事件桥等)触发的事件,处理数据后发送到目标系统。
Java Azure Function库提供基于注解的编程模型,用于:
- 注册方法到事件
- 接收源系统数据
- 更新目标系统
SCF框架为Azure Functions及其他无服务器服务(如AWS Lambda、Google Cloud Functions、Apache OpenWhisk)提供抽象层。这得益于SCF Azure适配器:
其统一编程模型确保代码跨平台可移植性,同时能将Spring框架的依赖注入等特性引入无服务器应用。
通常我们实现核心函数接口(如Function<I, O>、Consumer、Supplier
此外,SCF提供FunctionCatalog Bean,可通过*FunctionCatalog#lookup("<
3. 前置准备
首先需要有效的Azure订阅来部署应用。
Java应用需遵循Azure Functions编程模型,添加Maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-functions-java-library</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
代码完成后,使用Azure Functions Maven插件部署:
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-functions-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.24.0</version>
</plugin>
该插件将应用打包为Azure Functions要求的结构,可配置appname、resourcegroup等部署参数。
添加SCF库Maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-adapter-azure</artifactId>
<version>4.1.3</version>
</dependency>
该库在Java Azure Function处理器中启用SCF和Spring依赖注入功能。处理器指使用@FunctionName注解的方法,是处理Azure服务事件(如Blob存储、Cosmos DB事件桥等)的入口点。
应用JAR的Manifest文件需将入口点指向@SpringBootApplication注解的Spring Boot类。可通过maven-jar-plugin显式设置:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.baeldung.functions.AzureSpringCloudFunctionApplication</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
或设置pom.xml中的start-class属性(需使用spring-boot-starter-parent作为父级):
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.11</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<start-class>com.baeldung.functions.AzureSpringCloudFunctionApplication</start-class>
</properties>
最后,Azure要求特定打包格式,需禁用默认Spring Boot打包并启用spring boot thin layout:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot.experimental</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-thin-layout</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
4. Java实现
考虑一个场景:Azure Function应用根据员工居住城市计算津贴。通过HTTP接收员工JSON数据,添加津贴后返回。
4.1 基于普通Spring Bean的实现
首先定义核心类:
定义EmployeeSalaryFunction:
public class EmployeeSalaryFunction implements Function<Employee, Employee> {
@Override
public Employee apply(Employee employee) {
int allowance;
switch (employee.getCity()) {
case "Chicago" -> allowance = 5000;
case "California" -> allowance = 2000;
case "New York" -> allowance = 2500;
default -> allowance = 1000;
}
int finalSalary = employee.getSalary() + allowance;
employee.setSalary(finalSalary);
return employee;
}
}
该类实现java.util.function.Function接口,*在apply()*方法中根据城市添加津贴**。
在ApplicationConfiguration中注册为Spring Bean:
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfiguration {
@Bean
public Function<Employee, Employee> employeeSalaryFunction() {
return new EmployeeSalaryFunction();
}
}
@Configuration标记Bean定义源,*@Bean方法创建employeeSalaryFunction* Bean。
在EmployeeSalaryHandler中自动装配:
@Component
public class EmployeeSalaryHandler {
@Autowired
private Function<Employee, Employee> employeeSalaryFunction;
@FunctionName("employeeSalaryFunction")
public HttpResponseMessage calculateSalary(
@HttpTrigger(
name="http",
methods = HttpMethod.POST,
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS)HttpRequestMessage<Optional<Employee>> employeeHttpRequestMessage,
ExecutionContext executionContext
) {
Employee employeeRequest = employeeHttpRequestMessage.getBody().get();
Employee employee = employeeSalaryFunction.apply(employeeRequest);
return employeeHttpRequestMessage.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.body(employee)
.build();
}
}
事件处理器遵循Java Azure Function SDK模型,但使用Spring的@Component*和@Autowired注解**。建议自动装配的Bean名与@FunctionName*值一致。
类似地,可为其他触发器(如*@BlobTrigger、@QueueTrigger*)添加Spring支持。
4.2 基于SCF的实现
当需要动态获取函数Bean时,显式自动装配所有函数并非最优方案。
假设有多个城市薪资计算实现:
定义NewYorkSalaryCalculatorFn、ChicagoSalaryCalculatorFn和CaliforniaSalaryCalculatorFn等函数。以CaliforniaSalaryCalculatorFn为例:
public class CaliforniaSalaryCalculatorFn implements Function<Employee, Employee> {
@Override
public Employee apply(Employee employee) {
Integer finalSalary = employee.getSalary() + 3000;
employee.setSalary(finalSalary);
return employee;
}
}
该方法在基础薪资上添加*$3000*津贴。其他城市实现类似。
*入口方法EmployeeSalaryHandler#calculateSalaryWithSCF()使用EmployeeSalaryFunctionWrapper#getCityBasedSalaryFunction()*获取对应城市的薪资计算函数**:
public class EmployeeSalaryFunctionWrapper {
private FunctionCatalog functionCatalog;
public EmployeeSalaryFunctionWrapper(FunctionCatalog functionCatalog) {
this.functionCatalog = functionCatalog;
}
public Function<Employee, Employee> getCityBasedSalaryFunction(Employee employee) {
Function<Employee, Employee> salaryCalculatorFunction;
switch (employee.getCity()) {
case "Chicago" -> salaryCalculatorFunction = functionCatalog.lookup("chicagoSalaryCalculatorFn");
case "California" -> salaryCalculatorFunction = functionCatalog.lookup("californiaSalaryCalculatorFn|defaultSalaryCalculatorFn");
case "New York" -> salaryCalculatorFunction = functionCatalog.lookup("newYorkSalaryCalculatorFn");
default -> salaryCalculatorFunction = functionCatalog.lookup("defaultSalaryCalculatorFn");
}
return salaryCalculatorFunction;
}
}
通过构造函数注入FunctionCatalog,调用*getCityBasedSalaryFunction()获取正确函数。FunctionCatalog#lookup(<
函数Bean是SimpleFunctionRegistry$FunctionInvocationWrapper实例,支持函数组合和路由。例如:
functionCatalog.lookup("californiaSalaryCalculatorFn|defaultSalaryCalculatorFn")
返回的组合函数等价于:
californiaSalaryCalculatorFn.andThen(defaultSalaryCalculatorFn).apply(employee)
即加州员工同时获得州津贴和默认津贴。
最后看事件处理器:
@Component
public class EmployeeSalaryHandler {
@Autowired
private FunctionCatalog functionCatalog;
@FunctionName("calculateSalaryWithSCF")
public HttpResponseMessage calculateSalaryWithSCF(
@HttpTrigger(
name="http",
methods = HttpMethod.POST,
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS)HttpRequestMessage<Optional<Employee>> employeeHttpRequestMessage,
ExecutionContext executionContext
) {
Employee employeeRequest = employeeHttpRequestMessage.getBody().get();
executionContext.getLogger().info("Salary of " + employeeRequest.getName() + " is:" + employeeRequest.getSalary());
EmployeeSalaryFunctionWrapper employeeSalaryFunctionWrapper = new EmployeeSalaryFunctionWrapper(functionCatalog);
Function<Employee, Employee> cityBasedSalaryFunction = employeeSalaryFunctionWrapper.getCityBasedSalaryFunction(employeeRequest);
Employee employee = cityBasedSalaryFunction.apply(employeeRequest);
executionContext.getLogger().info("Final salary of " + employee.getName() + " is:" + employee.getSalary());
return employeeHttpRequestMessage.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.body(employee)
.build();
}
}
与前一节的calculateSalary()不同,此处使用自动装配的FunctionCatalog对象。
5. 部署与运行
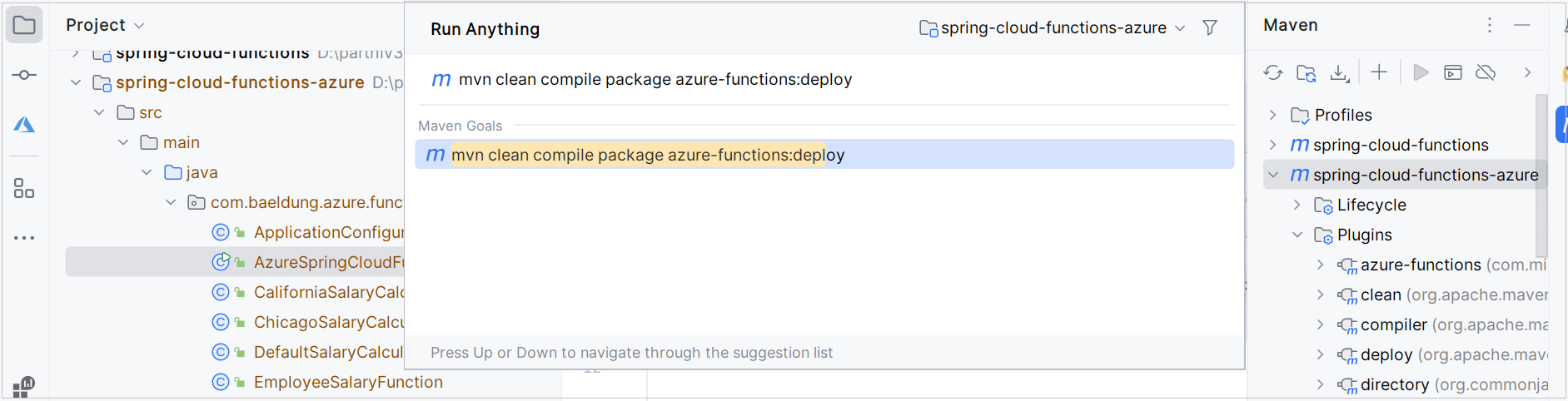
使用Maven编译、打包并部署到Azure Functions。在IntelliJ中运行Maven目标:
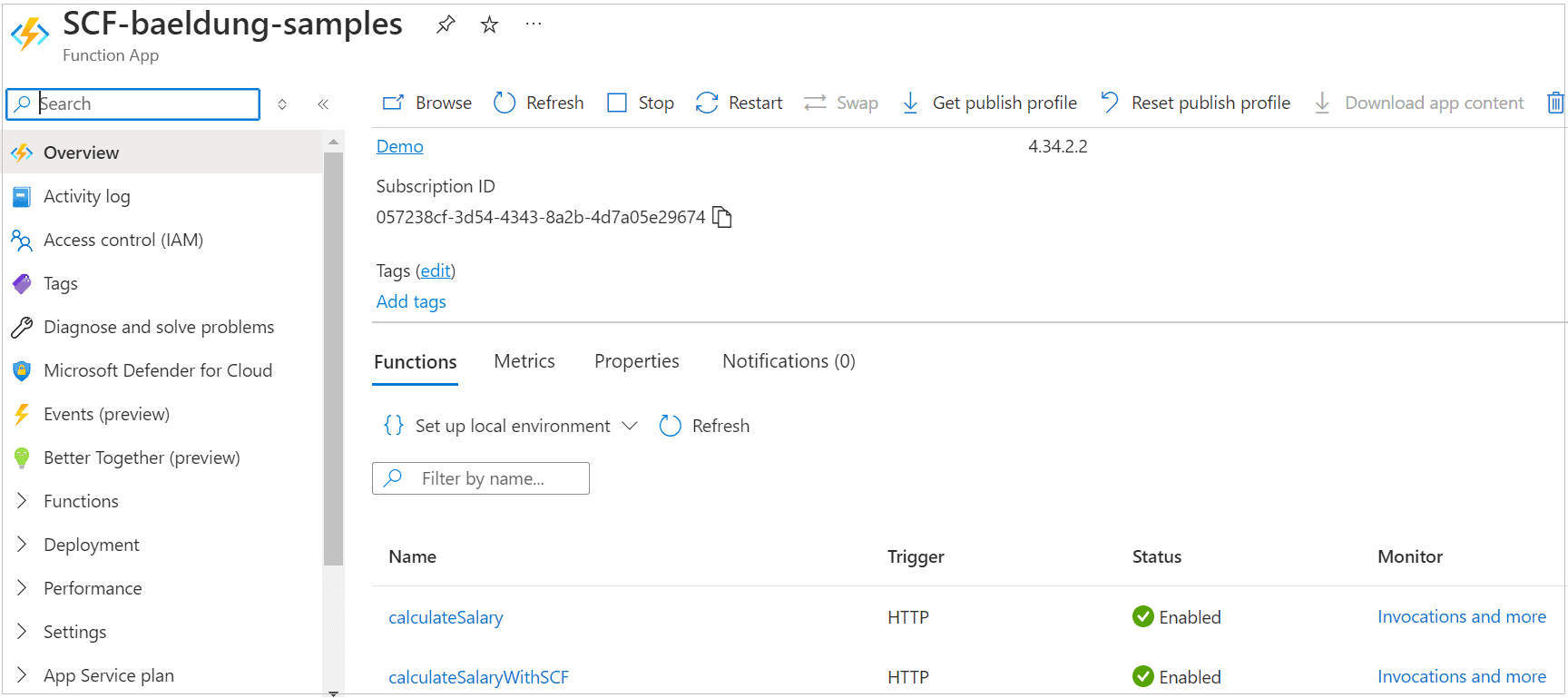
部署成功后,函数出现在Azure门户:
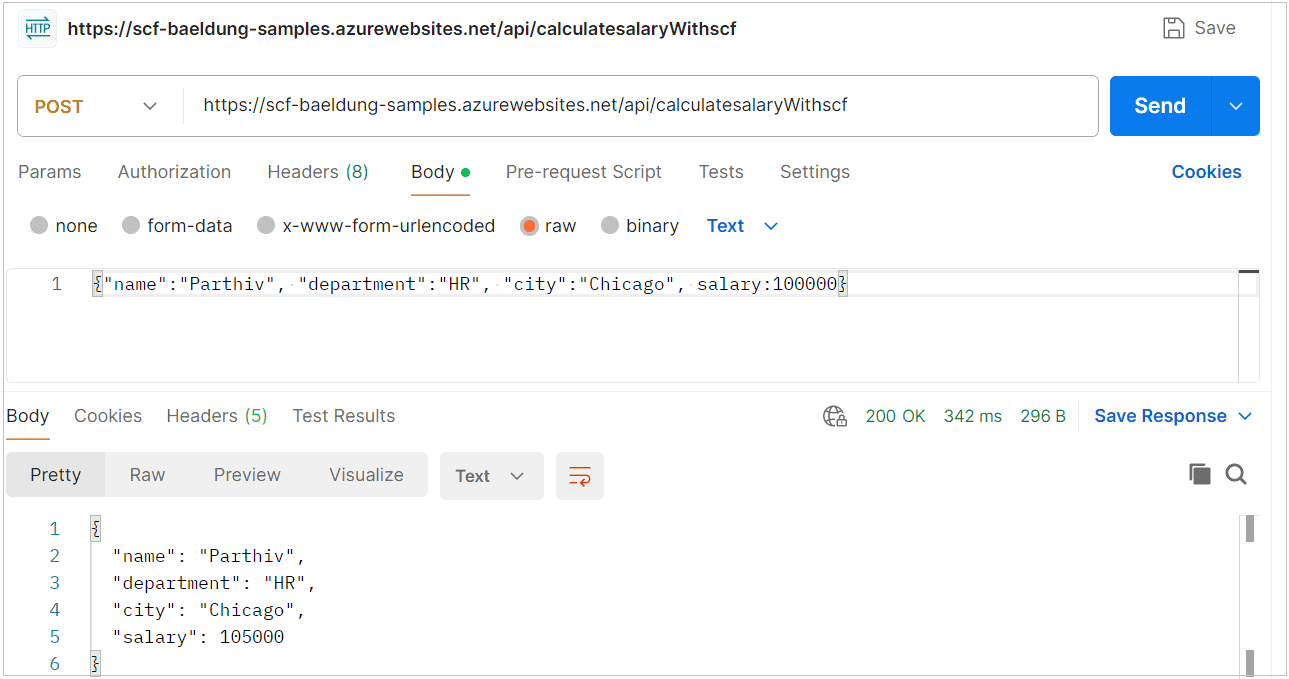
从Azure门户获取接口地址后,调用并验证结果:
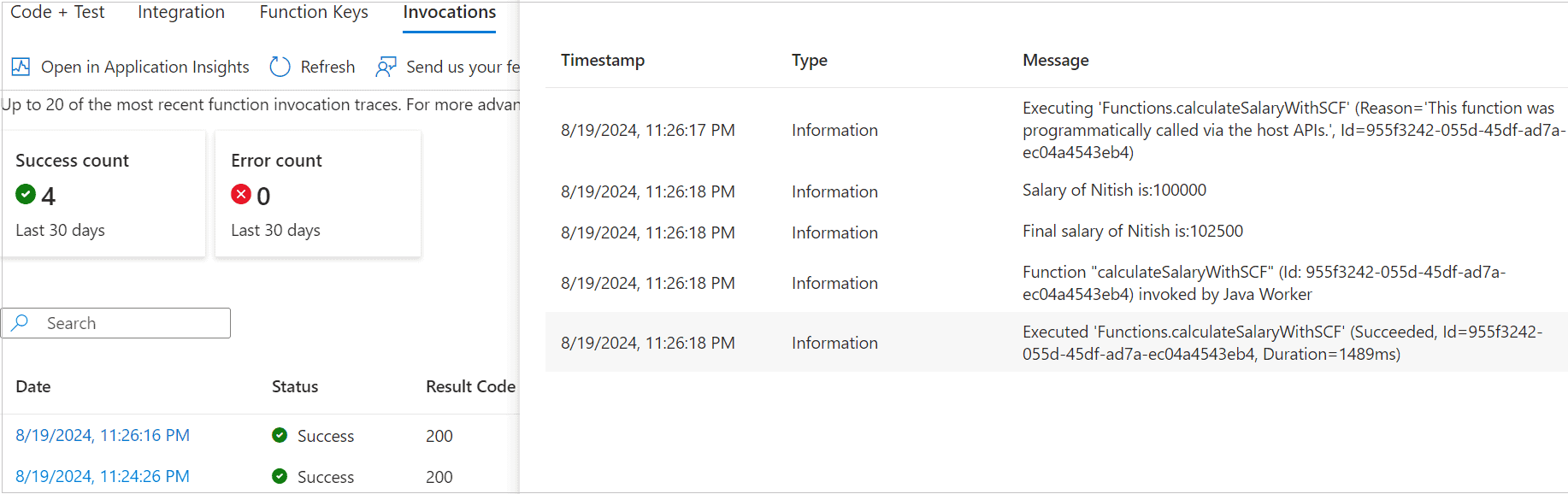
函数调用记录可在Azure门户确认:
6. 总结
本文介绍了使用Spring Cloud Function框架开发Java Azure Function应用的方法。该框架支持Spring依赖注入,FunctionCatalog类提供函数组合和路由功能。
⚠️ 虽然相比底层Java Azure Function库会增加一些开销,但能带来显著的设计优势。建议根据应用性能需求谨慎评估后采用。
完整代码可在GitHub获取。