1. 引言
Spring Cloud Gateway 是一个基于 Spring Boot 的轻量级 API 网关库,我们在之前的文章中已经详细介绍过。本文将重点演示如何在 Spring Cloud Gateway 上快速实现 OAuth 2.0 安全模式。
2. OAuth 2.0 快速回顾
OAuth 2.0 是互联网广泛采用的安全标准,用于实现用户和应用的安全资源访问。虽然本文不会深入展开标准细节,但先快速回顾几个关键术语:
- 资源:只有授权客户端才能访问的任何信息
- 客户端:消费资源的应用,通常通过 REST API 实现
- 资源服务器:负责向授权客户端提供资源的服务
- 资源所有者:拥有资源的实体(人或应用),最终负责授权客户端访问
- 令牌:客户端获取并在请求中发送给资源服务器用于认证的信息片段
- **身份提供者(IdP)**:验证用户凭据并向客户端颁发访问令牌
- 认证流程:客户端获取有效令牌必须执行的步骤序列
有关标准的完整描述,建议参考 Auth0 的官方文档。
3. OAuth 2.0 模式
Spring Cloud Gateway 主要用于以下两种角色:
- OAuth 客户端
- OAuth 资源服务器
下面详细讨论这两种场景。
3.1. Spring Cloud Gateway 作为 OAuth 2.0 客户端
此场景下,任何未认证的请求都会触发授权码流程。网关获取令牌后,会在转发请求到后端服务时使用该令牌:
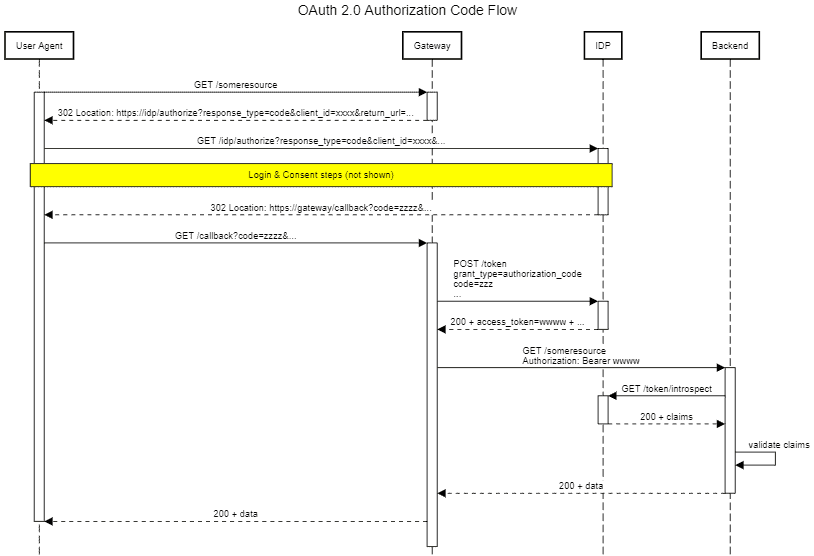
典型应用场景是社交网络聚合器:网关为每个支持的社交网络扮演 OAuth 2.0 客户端角色。这样前端(通常是用 Angular/React 等框架构建的 SPA)就能代表用户无缝访问这些网络的数据。更重要的是:用户无需向聚合器暴露自己的凭据。
3.2. Spring Cloud Gateway 作为 OAuth 2.0 资源服务器
网关在此充当守门人角色,强制要求每个请求必须携带有效访问令牌才能转发到后端服务。此外,它还能根据令牌关联的权限范围(scope)检查令牌是否有权访问特定资源:
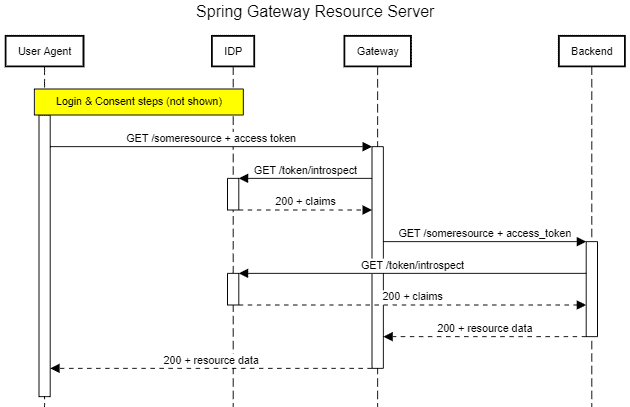
需要注意,这种权限检查主要在粗粒度级别进行。细粒度访问控制(如对象/字段级权限)通常在后端通过领域逻辑实现。此模式中需考虑后端服务如何认证和授权转发请求,主要有两种方式:
- 令牌传播:API 网关原样转发接收到的令牌
- 令牌替换:API 网关在发送请求前替换传入令牌
本文只覆盖令牌传播场景,因为这是最常见的模式。令牌替换虽然可行,但需要额外配置和编码,会偏离本文核心目标。
4. 示例项目概述
为演示 Spring Gateway 如何实现上述 OAuth 模式,我们将构建一个暴露 /quotes/{symbol} 接口的示例项目。访问该接口需要身份提供者颁发的有效访问令牌。
我们使用嵌入式 Keycloak 身份提供者。只需添加新客户端应用和测试用户即可。
为增加趣味性,后端服务会根据请求关联的用户返回不同报价:拥有 gold 角色的用户享受折扣价,其他用户支付常规价(生活本就不公平,^_^)。
我们将用 Spring Cloud Gateway 代理该服务,仅需修改几行配置,就能在 OAuth 客户端和资源服务器角色间切换。
5. 项目搭建
5.1. Keycloak 身份提供者
本教程使用的嵌入式 Keycloak 是个普通 SpringBoot 应用,可从 GitHub 克隆并用 Maven 构建:
$ git clone https://github.com/Baeldung/spring-security-oauth
$ cd oauth-rest/oauth-authorization/server
$ mvn install
注意:项目当前要求 Java 13+,但在 Java 11 下也能正常构建运行,只需在 Maven 命令中添加 -Djava.version=11。
接下来,替换 src/main/resources/baeldung-domain.json 为这个配置文件。修改版包含原配置所有内容,并新增了客户端应用(quotes-client)、两个用户组(golden_和silver_customers)以及两个角色(gold和silver)。
现在使用 spring-boot:run 插件启动服务器:
$ mvn spring-boot:run
... 省略大量日志
2022-01-16 10:23:20.318
INFO 8108 --- [ main] c.baeldung.auth.AuthorizationServerApp : Started AuthorizationServerApp in 23.815 seconds (JVM running for 24.488)
2022-01-16 10:23:20.334
INFO 8108 --- [ main] c.baeldung.auth.AuthorizationServerApp : Embedded Keycloak started: http://localhost:8083/auth to use keycloak
服务器启动后,通过浏览器访问 http://localhost:8083/auth/admin/master/console/#/realms/baeldung。使用管理员凭据(bael-admin/pass)登录后进入领域管理界面:
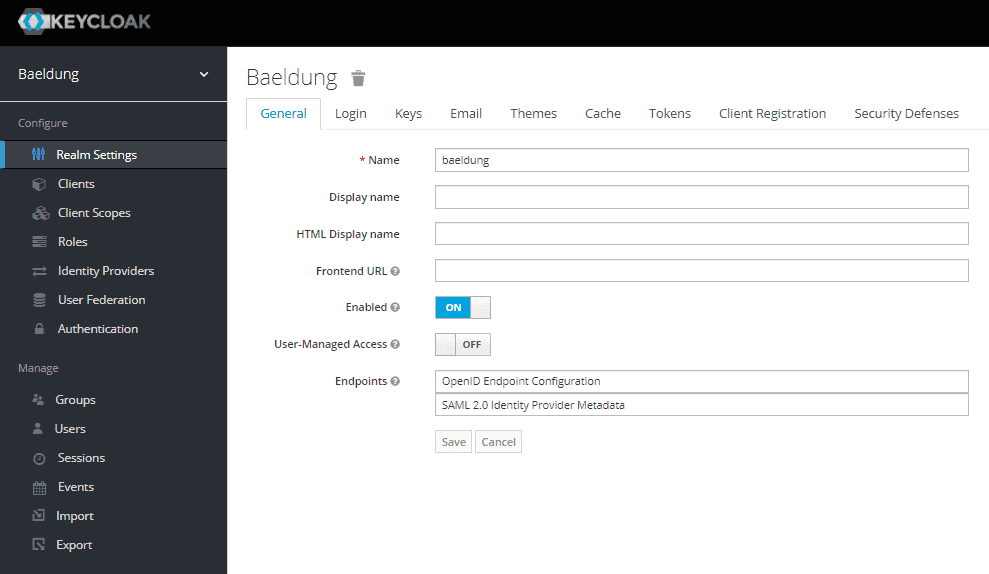
最后添加两个用户:第一个是 golden_customer 组成员 Maxwell Smart;第二个是 John Snow(不加入任何组)。根据配置,golden_customers 组成员会自动获得 gold 角色。
5.2. 后端服务
报价后端需要常规 Spring Boot Reactive MVC 依赖,加上资源服务器启动器依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意:我们省略了依赖版本号,这是使用 SpringBoot 父 POM 或 BOM 时的推荐做法。
在主应用类添加 @EnableWebFluxSecurity 启用 WebFlux 安全:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class QuotesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(QuotesApplication.class);
}
}
接口实现使用 BearerAuthenticationToken 检查当前用户是否拥有 gold 角色:
@RestController
public class QuoteApi {
private static final GrantedAuthority GOLD_CUSTOMER = new SimpleGrantedAuthority("gold");
@GetMapping("/quotes/{symbol}")
public Mono<Quote> getQuote(@PathVariable("symbol") String symbol,
BearerTokenAuthentication auth ) {
Quote q = new Quote();
q.setSymbol(symbol);
if ( auth.getAuthorities().contains(GOLD_CUSTOMER)) {
q.setPrice(10.0);
}
else {
q.setPrice(12.0);
}
return Mono.just(q);
}
}
Spring 如何获取用户角色?毕竟这不是像 scopes 或 email 那样的标准声明。这需要自定义 ReactiveOpaqueTokenIntrospection Bean 从 Keycloak 返回的自定义字段中提取角色。该 Bean 基本与 Spring官方文档示例一致,仅针对自定义字段做了微调。
还需提供身份提供者的配置属性:
spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.introspection-uri=http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect
spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.client-id=quotes-client
spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.client-secret=0e082231-a70d-48e8-b8a5-fbfb743041b6
最后通过 Maven 运行应用(项目 POM 包含专用 profile):
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Pquotes-application
应用将在 http://localhost:8085/quotes 提供服务。用 curl 验证响应:
$ curl -v http://localhost:8085/quotes/BAEL
意料之中:未发送 Authorization 头,收到 401 Unauthorized 响应。
6. Spring Gateway 作为 OAuth 2.0 资源服务器
保护作为资源服务器的 Spring Cloud Gateway 应用 与普通资源服务器无异。因此需添加与后端服务相同的启动器依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
同样在启动类添加 @EnableWebFluxSecurity:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class ResourceServerGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ResourceServerGatewayApplication.class,args);
}
}
安全配置属性与后端服务一致:
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
opaquetoken:
introspection-uri: http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect
client-id: quotes-client
client-secret: 0e082231-a70d-48e8-b8a5-fbfb743041b6
路由配置与我们前一篇 Spring Cloud Gateway 文章相同:
... 其他属性省略
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: quotes
uri: http://localhost:8085
predicates:
- Path=/quotes/**
注意:除了安全依赖和属性,网关本身无需任何修改。使用专用 profile 启动网关:
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Pgateway-as-resource-server
6.1. 测试资源服务器
现在整合所有组件:确保 Keycloak、报价后端和网关都在运行。
首先需要从 Keycloak 获取访问令牌。最简单的方式是使用密码授权模式(Resource Owner 流程),向 Keycloak 发送 POST 请求,包含用户名/密码、客户端 ID 和密钥:
$ curl -L -X POST \
'http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung/protocol/openid-connect/token' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'client_id=quotes-client' \
--data-urlencode 'client_secret=0e082231-a70d-48e8-b8a5-fbfb743041b6' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=password' \
--data-urlencode 'scope=email roles profile' \
--data-urlencode 'username=john.snow' \
--data-urlencode 'password=1234'
响应是包含访问令牌的 JSON 对象:
{
"access_token": "...省略...",
"expires_in": 300,
"refresh_expires_in": 1800,
"refresh_token": "...省略...",
"token_type": "bearer",
"not-before-policy": 0,
"session_state": "7fd04839-fab1-46a7-a179-a2705dab8c6b",
"scope": "profile email"
}
使用返回的访问令牌调用 /quotes 接口:
$ curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8086/quotes/BAEL' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer xxxx...'
返回 JSON 格式的报价:
{
"symbol":"BAEL",
"price":12.0
}
用 Maxwell Smart 的令牌重复测试:
{
"symbol":"BAEL",
"price":10.0
}
价格更低,说明后端正确识别了用户角色。再用不带 Authorization 头的 curl 验证未认证请求:
$ curl http://localhost:8086/quotes/BAEL
检查网关日志会发现没有请求转发相关记录,证明响应由网关直接生成。
7. Spring Gateway 作为 OAuth 2.0 客户端
启动类复用资源服务器版本。以此强调所有安全行为都来自库和配置。
两个版本的主要差异在于配置属性。这里需要通过 issuer-uri 或独立端点配置身份提供者详情(授权、令牌、内省端点)。
还需定义客户端注册详情,包括请求的范围(scope),这些范围告知 IdP 通过内省机制可提供哪些信息:
... 其他属性省略
security:
oauth2:
client:
provider:
keycloak:
issuer-uri: http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung
registration:
quotes-client:
provider: keycloak
client-id: quotes-client
client-secret: 0e082231-a70d-48e8-b8a5-fbfb743041b6
scope:
- email
- profile
- roles
路由配置的关键修改:为需要传播令牌的路由添加 TokenRelay 过滤器:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: quotes
uri: http://localhost:8085
predicates:
- Path=/quotes/**
filters:
- TokenRelay=
若所有路由都需要触发认证流程,可将 TokenRelay 添加到 default-filters:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
default-filters:
- TokenRelay=
routes:
... 其他路由省略
7.1. 测试 Spring Gateway 作为 OAuth 2.0 客户端
测试前确保三个组件都在运行。这次用不同 Spring Profile 启动网关,使其扮演 OAuth 2.0 客户端角色。项目 POM 包含专用 profile:
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Pgateway-as-oauth-client
网关启动后,浏览器访问 http://localhost:8087/quotes/BAEL。若一切正常,会重定向到 IdP 登录页:
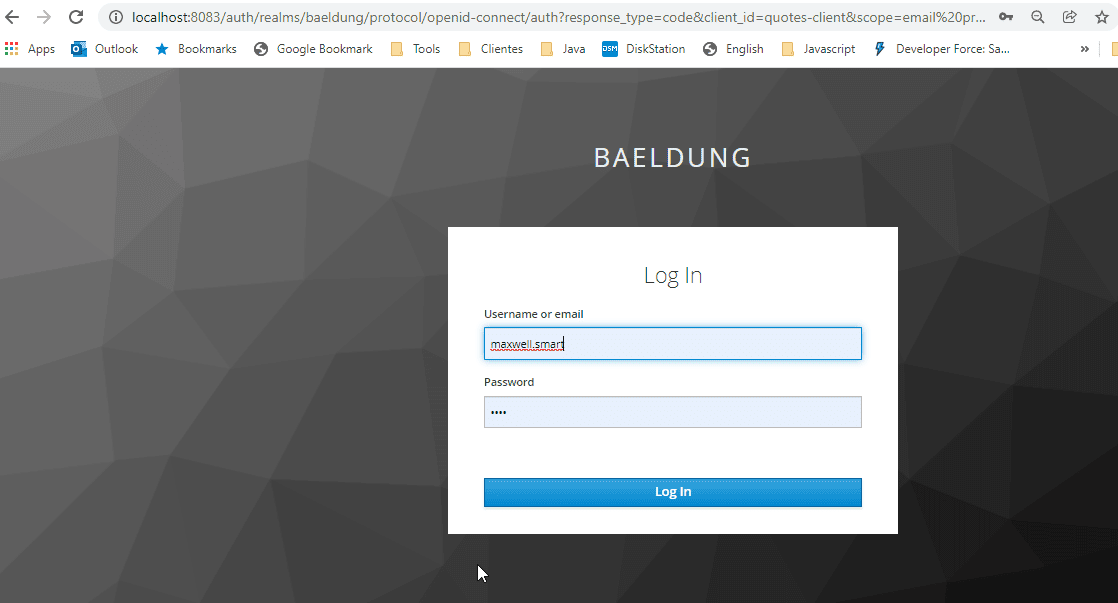
使用 Maxwell Smart 凭据登录后,获得折扣价报价:
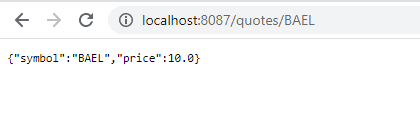
最后用无痕窗口测试 John Snow 的凭据,获得常规报价:
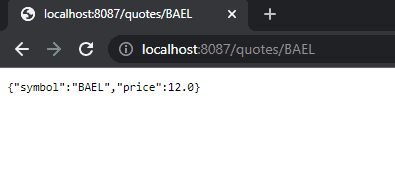
8. 结论
本文探讨了 OAuth 2.0 的几种安全模式,以及如何用 Spring Cloud Gateway 实现它们。所有代码可在 GitHub 获取。