1. 概述
✅ Spring REST Docs 和 ✅ OpenAPI 3.0 是当前主流的两种 REST API 文档生成方案。
本文将从实践角度对比两者的核心差异,帮助你在项目中做出合理选择——是追求“文档即测试”的严谨性,还是青睐“开箱即用”的便捷性。
2. 起源与设计理念
2.1 Spring REST Docs
- 测试驱动文档(TDD):文档通过单元测试生成,测试通过意味着接口行为正确 ✅
- 输出为 AsciiDoc:测试运行后生成
.adoc片段,再通过 Asciidoctor 拼接为静态 HTML - 核心优势:文档永远与代码同步,避免“文档过期”这种经典踩坑场景
⚠️ 由于依赖测试,文档内容由测试用例驱动,天然具备验证能力。
2.2 OpenAPI(原 Swagger)
- 规范驱动:基于 OpenAPI 3.0 规范,输出标准的 JSON/YAML 文件
- 生态丰富:支持大量可视化工具(如 Swagger UI、ReDoc)
- 代表实现:本文使用
springdoc-openapi(Spring Boot 场景下最主流方案)
✅ 所有 OpenAPI 实现都必须生成结构化的 API 描述文件,便于机器解析和 UI 渲染。
我们将在下文使用 springdoc 作为 OpenAPI 的代表实现进行演示。
3. 示例 REST API
我们构建一个基于 Spring Boot 的简单 CRUD 接口作为演示对象。
3.1 数据模型与仓库
@Repository
public interface FooRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Foo, Long> {}
@Entity
public class Foo {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column
private String body;
// 构造函数、getter/setter 省略
}
使用 schema.sql 和 data.sql 初始化数据。
3.2 控制器接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/foo")
public class FooController {
@Autowired
FooRepository repository;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Foo>> getAllFoos() {
// 实现省略
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Foo> getFooById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
// 实现省略
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<Foo> addFoo(@RequestBody @Valid Foo foo) {
// 实现省略
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteFoo(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
// 实现省略
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Foo> updateFoo(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestBody Foo foo) {
// 实现省略
}
}
3.3 启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
4. OpenAPI + springdoc 实践
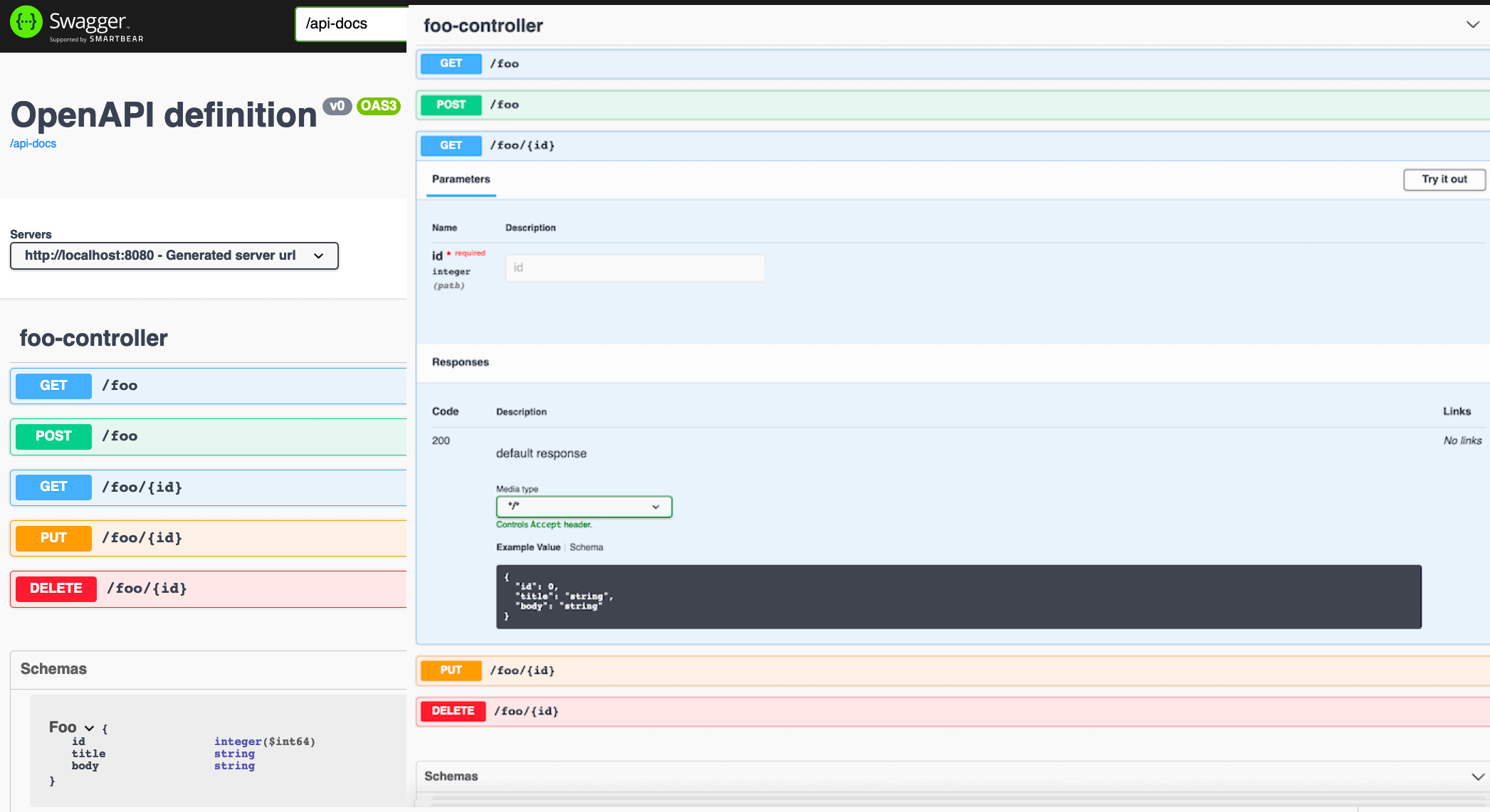
springdoc 能自动扫描代码注解,生成 OpenAPI JSON 并提供可视化 UI。
4.1 基础 UI 集成
添加 Maven 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-data-rest</artifactId>
<version>1.6.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.6.14</version>
</dependency>
启动后访问:
- OpenAPI JSON:
http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs - Swagger UI:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
✅ 无需任何配置,自动生成接口列表和 Foo 模型结构,支持“Try it out”在线调试。
4.2 添加详细文档
全局 API 信息
通过配置 OpenAPI Bean 添加元数据:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI(@Value("${springdoc.version}") String appVersion) {
return new OpenAPI().info(new Info()
.title("Foobar API")
.version(appVersion)
.description("This is a sample Foobar server created using springdocs - " +
"a library for OpenAPI 3 with spring boot.")
.termsOfService("http://swagger.io/terms/")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0")
.url("http://springdoc.org")));
}
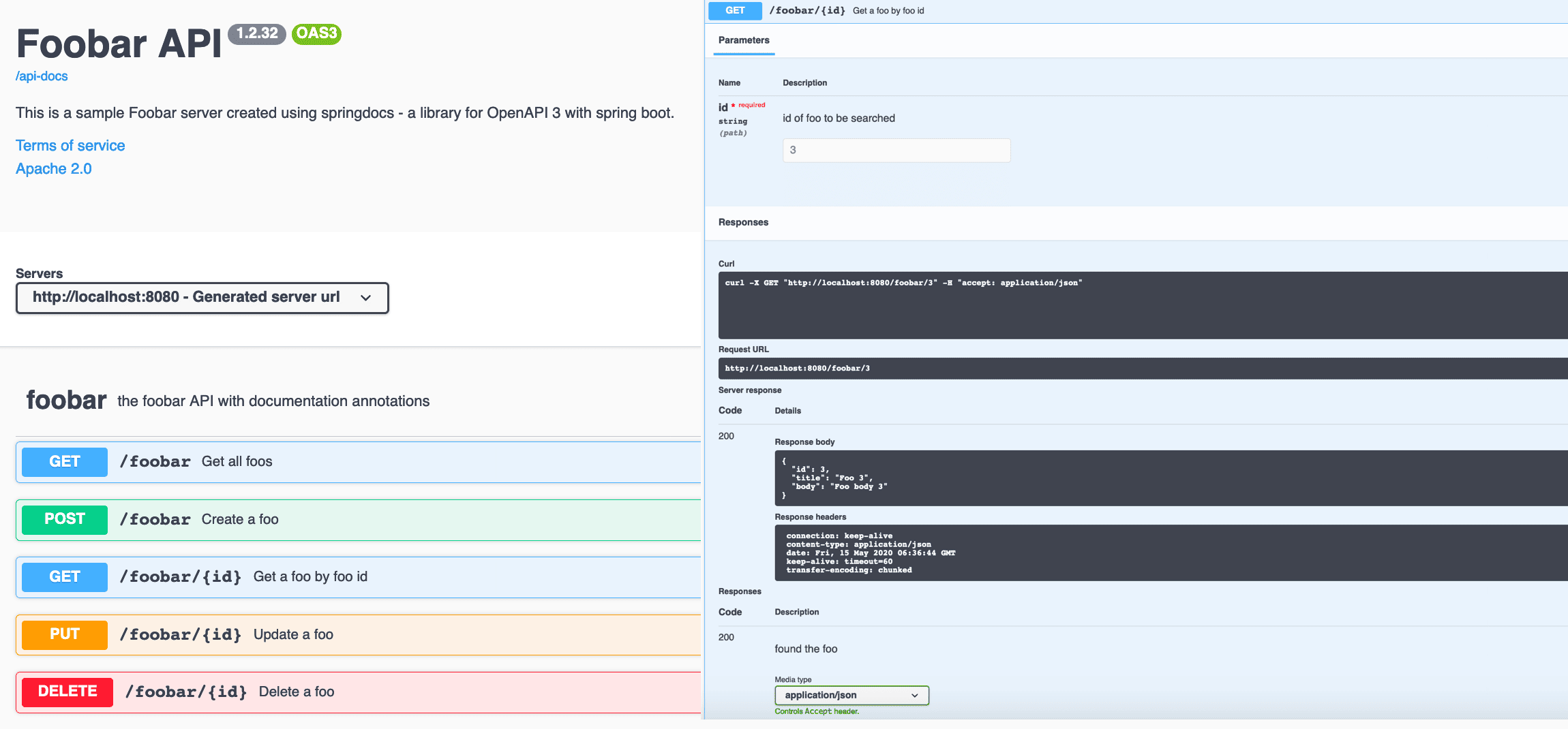
接口级文档注解
使用 OpenAPI 注解丰富接口描述:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/foobar")
@Tag(name = "foobar", description = "the foobar API with documentation annotations")
public class FooBarController {
@Autowired
FooRepository repository;
@Operation(summary = "Get a foo by foo id")
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "found the foo",
content = { @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = Foo.class))}),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "Invalid id supplied", content = @Content),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Foo not found", content = @Content) })
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Foo> getFooById(
@Parameter(description = "id of foo to be searched") @PathVariable("id") String id) {
// 实现省略
}
}
效果如下:
✅ 用户可清晰了解接口用途、参数说明、响应码含义。
5. Spring REST Docs 实践
5.1 Maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.restdocs</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-restdocs-mockmvc</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Maven 插件(用于生成 HTML):
<plugin>
<groupId>org.asciidoctor</groupId>
<artifactId>asciidoctor-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>generate-docs</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>process-asciidoc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
5.2 编写测试生成文档片段
@ExtendWith({ RestDocumentationExtension.class, SpringExtension.class })
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class SpringRestDocsIntegrationTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@BeforeEach
public void setup(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext,
RestDocumentationContextProvider restDocumentation) {
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(webApplicationContext)
.apply(documentationConfiguration(restDocumentation))
.build();
}
@Test
public void whenGetFooById_thenSuccessful() throws Exception {
ConstraintDescriptions desc = new ConstraintDescriptions(Foo.class);
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/foo/{id}", 1))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(document("getAFoo",
preprocessRequest(prettyPrint()),
preprocessResponse(prettyPrint()),
pathParameters(
parameterWithName("id").description("id of foo to be searched")
),
responseFields(
fieldWithPath("id")
.description("The id of the foo" +
collectionToDelimitedString(desc.descriptionsForProperty("id"), ". ")),
fieldWithPath("title").description("The title of the foo"),
fieldWithPath("body").description("The body of the foo")
)));
}
}
运行测试后,生成的文档片段位于 target/generated-snippets/getAFoo/ 目录下。
示例:http-response.adoc
[source,http,options="nowrap"]
----
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 60
{
"id" : 1,
"title" : "Foo 1",
"body" : "Foo body 1"
}
----
5.3 汇总为完整文档(fooapi.adoc)
=== Accessing the foo GET
A `GET` request is used to access the foo read.
==== Request structure
include::{snippets}/getAFoo/http-request.adoc[]
==== Path Parameters
include::{snippets}/getAFoo/path-parameters.adoc[]
==== Example response
include::{snippets}/getAFoo/http-response.adoc[]
==== CURL request
include::{snippets}/getAFoo/curl-request.adoc[]
执行 mvn asciidoctor:process-asciidoc 后,生成 target/generated-docs/fooapi.html。
效果预览:
6. 核心对比总结
| 维度 | OpenAPI + springdoc | Spring REST Docs |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ 文档准确性 | ❌ 依赖人工维护注解 | ✅ 由测试保证,永远最新 |
| ✅ 开发效率 | ✅ 零配置即用,支持热加载 | ❌ 需写测试 + 维护 .adoc 文件 |
| ✅ 可读性 | ❌ 注解污染业务代码 | ✅ 文档与代码完全分离 |
| ✅ 可视化体验 | ✅ 提供交互式 UI,支持调试 | ❌ 静态 HTML,体验较原始 |
| ✅ 适用场景 | 内部服务、快速原型、前后端联调 | 对外开放 API、合同测试、文档归档 |
简单粗暴选型建议:
- 如果你追求 快速出文档 + 在线调试 → 选
springdoc - 如果你重视 文档权威性 + 自动化验证 → 选
Spring REST Docs
7. 结论
- ✅ OpenAPI 适合敏捷开发、内部系统,强调“速度”与“交互”
- ✅ Spring REST Docs 适合对外 API、金融级系统,强调“准确”与“契约”
两者并非互斥,大型项目可结合使用:用 REST Docs 生成权威合同文档,用 OpenAPI 提供开发调试 UI。
源码地址:https://github.com/baeldung/tutorials/tree/master/spring-boot-modules/spring-boot-springdoc