1. 概述
本文将详细介绍 如何使用 Spring Security 5 构建一个 OAuth 2.0 资源服务器。
我们将分别实现两种主流的令牌验证方式:
✅ JWT(JSON Web Token)
✅ Opaque Token(不透明令牌)
在进入代码实现之前,先快速梳理一下背景知识,确保理解底层逻辑。毕竟踩过坑才知道,光会配置不理解原理,出问题时根本无从下手。
2. 背景知识
2.1 JWT 与 Opaque Token 的区别
- JWT:是一种自包含的令牌格式(遵循 RFC 7519),以 JSON 结构明文携带用户信息、过期时间、签发者等元数据。资源服务器可直接解析并验证签名,无需每次都调用授权服务器。
- Opaque Token:顾名思义,内容对外“不透明”,只是一个随机字符串。它本身不包含任何有效信息,资源服务器必须通过 Token Introspection 接口向授权服务器发起请求,查询该令牌是否有效、权限如何。
🔍 简单粗暴理解:JWT 是“自带身份证”,Opaque Token 是“需要联网查号”。
2.2 什么是资源服务器(Resource Server)
在 OAuth 2.0 体系中,资源服务器是负责保护受保护资源的服务应用。它不负责发令牌,只负责验令牌。
当客户端携带 Authorization: Bearer <token> 请求资源时,资源服务器需验证以下几点:
- ✅ 令牌是否由可信的授权服务器签发
- ✅ 是否已过期
- ✅ 当前服务是否是目标受众(audience)
- ✅ 是否具备访问该资源所需的权限(如 scope)
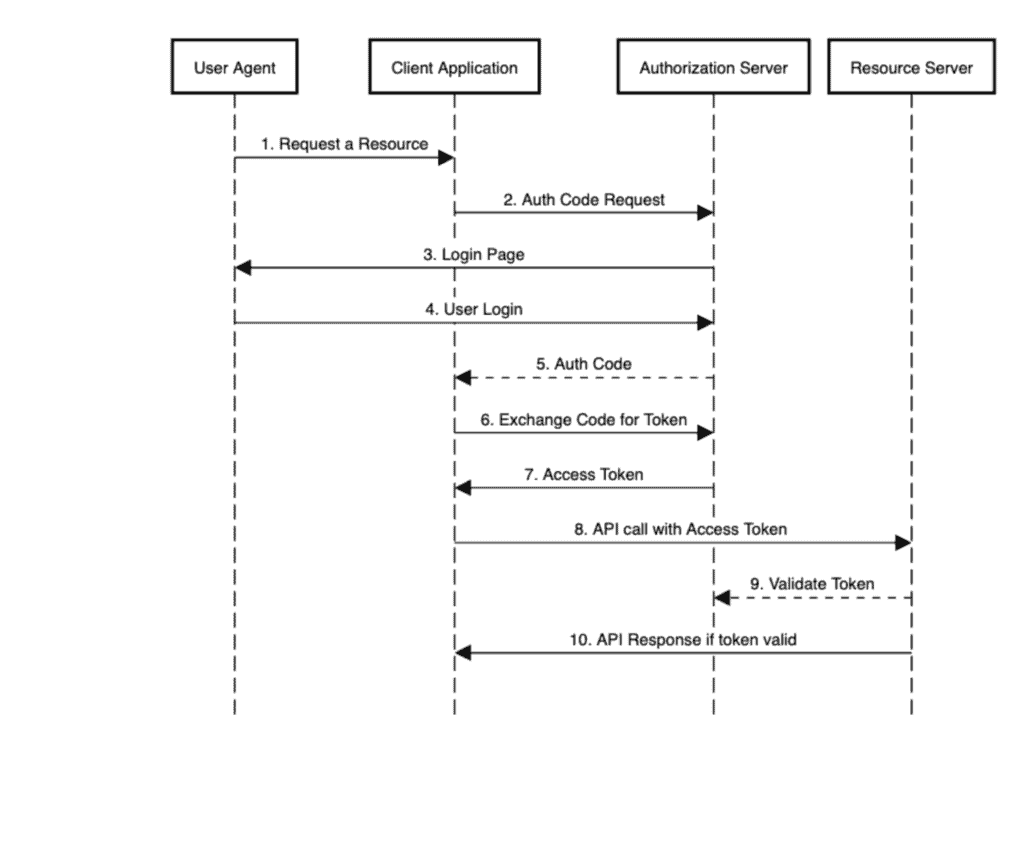
下面是典型的授权码流程时序图,我们重点关注第 8、9 步:
图中第 8 步:客户端调用资源服务器
第 9 步:资源服务器向授权服务器验证令牌(本文重点)
3. 授权服务器搭建(Keycloak 嵌入式)
我们使用 Keycloak 作为授权服务器。它是开源的身份与访问管理方案,支持 OpenID Connect 和 OAuth 2.0。
💡 本文重点在资源服务器,因此 Keycloak 的配置细节不再展开。感兴趣可参考:《Spring Boot 集成嵌入式 Keycloak》
我们预设了两个客户端:
fooClient→ 对应 JWT 资源服务器barClient→ 对应 Opaque Token 资源服务器
Keycloak 运行在 http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung
4. 资源服务器 – 使用 JWT
4.1 Maven 依赖
核心依赖是 spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server,它自动引入 Spring Security 并提供资源服务器支持。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.13.0</version>
</dependency>
⚠️ 注意:无需显式引入
spring-security-*,starter 已包含。
4.2 模型类(Model)
定义一个简单的 POJO 作为受保护资源:
public class Foo {
private long id;
private String name;
// 构造函数、getter、setter 省略
}
4.3 接口层(API)
提供 REST 接口供客户端操作 Foo 资源:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/foos")
public class FooController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Foo findOne(@PathVariable Long id) {
return new Foo(Long.parseLong(randomNumeric(2)), randomAlphabetic(4));
}
@GetMapping
public List<Foo> findAll() {
List<Foo> fooList = new ArrayList<>();
fooList.add(new Foo(Long.parseLong(randomNumeric(2)), randomAlphabetic(4)));
fooList.add(new Foo(Long.parseLong(randomNumeric(2)), randomAlphabetic(4)));
fooList.add(new Foo(Long.parseLong(randomNumeric(2)), randomAlphabetic(4)));
return fooList;
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
@PostMapping
public void create(@RequestBody Foo newFoo) {
logger.info("Foo created");
}
}
支持:GET 单个、GET 列表、POST 创建。
4.4 安全配置(Security Configuration)
关键配置类,定义访问控制策略:
@Configuration
public class JWTSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests(authz -> authz
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/foos/**")
.hasAuthority("SCOPE_read")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/foos")
.hasAuthority("SCOPE_write")
.anyRequest()
.authenticated())
.oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> oauth2.jwt());
return http.build();
}
}
- GET 请求需具备
SCOPE_read权限 - POST 请求需具备
SCOPE_write权限 .oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> oauth2.jwt())明确声明支持 JWT 令牌
✅ 注意:Spring Security 5.4+ 使用
SecurityFilterChain替代旧版WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
4.5 配置文件(application.yml)
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /resource-server-jwt
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
jwt:
issuer-uri: http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung
issuer-uri指定授权服务器地址,Spring 会自动获取其 OpenID Connect 提供商配置(如 JWK Set URI)- 启动时会自动拉取公钥用于验证 JWT 签名
⚠️ 若授权服务器未启动,资源服务器将无法初始化。若需独立部署,可改用
jwk-set-uri:
jwk-set-uri: http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung/protocol/openid-connect/certs
4.6 测试验证
使用 JUnit + RestAssured 模拟客户端请求:
@Test
public void givenUserWithReadScope_whenGetFooResource_thenSuccess() {
String accessToken = obtainAccessToken("read"); // 从 Keycloak 获取带 read scope 的 token
Response response = RestAssured.given()
.header(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION, "Bearer " + accessToken)
.get("http://localhost:8081/resource-server-jwt/foos");
assertThat(response.as(List.class)).hasSizeGreaterThan(0);
}
- ✅ 成功返回数据 → 表示 JWT 被正确验证并放行
- 整个过程透明,开发者无需手动处理 JWT 解析
5. 资源服务器 – 使用 Opaque Token
5.1 Maven 依赖
Opaque Token 需要额外依赖用于 Token Introspection:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.nimbusds</groupId>
<artifactId>oauth2-oidc-sdk</artifactId>
<version>8.19</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
⚠️ 注意:
runtime范围即可,编译期不需要。
5.2 模型与控制器
新增 Bar 资源:
public class Bar {
private long id;
private String name;
// 构造函数、getter、setter
}
控制器 BarController 提供 /bars 接口,结构与 FooController 类似。
5.3 配置文件(application.yml)
server:
port: 8082
servlet:
context-path: /resource-server-opaque
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
opaque:
introspection-uri: http://localhost:8083/auth/realms/baeldung/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect
introspection-client-id: barClient
introspection-client-secret: barClientSecret
introspection-uri:Keycloak 的令牌验证接口- 需提供客户端凭证用于调用该接口
5.4 安全配置
@Configuration
public class OpaqueSecurityConfig {
@Value("${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaque.introspection-uri}")
String introspectionUri;
@Value("${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaque.introspection-client-id}")
String clientId;
@Value("${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaque.introspection-client-secret}")
String clientSecret;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests(authz -> authz
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/bars/**")
.hasAuthority("SCOPE_read")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/bars")
.hasAuthority("SCOPE_write")
.anyRequest()
.authenticated())
.oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> oauth2.opaqueToken(token ->
token.introspectionUri(this.introspectionUri)
.introspectionClientCredentials(this.clientId, this.clientSecret)));
return http.build();
}
}
.opaqueToken()表示启用不透明令牌支持- 显式配置 introspection 地址和客户端凭据
5.5 测试验证
测试 write 权限是否能成功创建资源:
@Test
public void givenUserWithWriteScope_whenPostNewBarResource_thenCreated() {
String accessToken = obtainAccessToken("read write");
Bar newBar = new Bar(Long.parseLong(randomNumeric(2)), randomAlphabetic(4));
Response response = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.header(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION, "Bearer " + accessToken)
.body(newBar)
.log().all()
.post("http://localhost:8082/resource-server-opaque/bars");
assertThat(response.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.CREATED.value());
}
- ✅ 返回 201 → 表示 Opaque Token 被成功验证并授权
6. 总结
本文完整演示了如何使用 Spring Security 5 构建两种类型的 OAuth 2.0 资源服务器:
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ JWT | 无状态、高性能、无需网络调用 | 无法主动吊销 |
| ✅ Opaque Token | 可实时控制、支持吊销 | 每次请求需调用 introspection 接口,有性能开销 |
🎯 核心要点:
- Spring Security 的 DSL 配置极其简洁
- JWT 使用
.jwt(),Opaque 使用.opaqueToken()- 生产环境建议结合缓存优化 Opaque Token 的验证性能
所有示例代码已托管至 GitHub:https://github.com/Baeldung/spring-security-oauth/tree/master/oauth-resource-server