1. 概述
本文将带你快速掌握如何使用 Spring Session JDBC 模块,把用户的会话(Session)数据持久化到关系型数据库中。
为了演示方便,我们会使用内存中的 H2 数据库。整个过程简洁高效,适合在微服务或分布式架构中实现会话共享。
✅ 核心目标:解决传统 HttpSession 在多实例部署下的数据不一致问题
❌ 常见误区:认为 Spring Session 需要大量配置 —— 其实 Spring Boot 下一行配置就够了
2. 配置方式选择
搭建示例项目最简单的方式是使用 Spring Boot,但我们也提供纯 Spring 的非 Boot 配置方式。
⚠️ 注意:你只需要根据项目实际情况选择其中一种方式即可,不需要两个都做。
3. Spring Boot 方式配置
如果你正在使用 Spring Boot,那配置简直是简单粗暴到极致。
3.1 Maven 依赖
添加以下依赖项:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.214</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
📌 提示:Spring Boot 的 parent POM 已经管理了版本。最新版可参考 Maven Central。
3.2 application.properties 配置
关键来了 —— 只需在 application.properties 中加这一行:
spring.session.store-type=jdbc
✅ 就这么一行!Spring Boot 会自动完成以下事情:
- 创建
springSessionRepositoryFilter - 启用 JDBC 会话存储
- 自动执行建表脚本(基于数据库类型)
⚠️ 如果你用的是 MySQL 或 PostgreSQL,表结构会自动适配,但 H2 是最方便的测试选择。
4. 标准 Spring 配置(无 Boot)
如果你没用 Spring Boot,而是纯 Spring 项目,也可以手动配置。
4.1 Maven 依赖
确保 pom.xml 包含:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.214</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
4.2 配置类
创建一个配置类,启用 JDBC 会话支持:
@Configuration
@EnableJdbcHttpSession
public class Config extends AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer {
@Bean
public EmbeddedDatabase dataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()
.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2)
.addScript("org/springframework/session/jdbc/schema-h2.sql")
.build();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
📌 要点说明:
@EnableJdbcHttpSession是核心注解,启用 JDBC 会话持久化EmbeddedDatabase手动构建内存数据库并执行建表脚本transactionManager保证会话操作的事务性- 继承
AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer会自动注册springSessionRepositoryFilter
💡 对比 Boot:少了自动配置,多了显式 Bean 定义,但逻辑完全一致。
5. 简单应用示例
我们来写个简单的 REST 接口,实现“保存用户喜欢的颜色”功能,验证会话是否真的持久化了。
5.1 控制器代码
@Controller
public class SpringSessionJdbcController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model, HttpSession session) {
List<String> favoriteColors = getFavColors(session);
model.addAttribute("favoriteColors", favoriteColors);
model.addAttribute("sessionId", session.getId());
return "index";
}
@PostMapping("/saveColor")
public String saveMessage(
@RequestParam("color") String color,
HttpServletRequest request) {
List<String> favoriteColors = getFavColors(request.getSession());
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(color)) {
favoriteColors.add(color);
request.getSession().setAttribute("favoriteColors", favoriteColors);
}
return "redirect:/";
}
private List<String> getFavColors(HttpSession session) {
List<String> favoriteColors = (List<String>) session.getAttribute("favoriteColors");
if (favoriteColors == null) {
favoriteColors = new ArrayList<>();
}
return favoriteColors;
}
}
📌 说明:
- GET
/:读取当前会话中的颜色列表 - POST
/saveColor:添加新颜色并重定向 - 使用
HttpSessionAPI 完全不变 —— 这正是 Spring Session 的优雅之处:对业务代码透明
6. 测试验证
我们通过集成测试验证会话是否真正写入数据库。
6.1 测试类基础结构
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@FixMethodOrder(MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING)
public class SpringSessionJdbcApplicationTests {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
private List<String> getSessionIdsFromDatabase() throws SQLException {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSet rs = getResultSet("SELECT * FROM SPRING_SESSION");
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rs.getString("SESSION_ID"));
}
return result;
}
private List<byte[]> getSessionAttributeBytesFromDb() throws SQLException {
List<byte[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
ResultSet rs = getResultSet("SELECT * FROM SPRING_SESSION_ATTRIBUTES");
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rs.getBytes("ATTRIBUTE_BYTES"));
}
return result;
}
private ResultSet getResultSet(String sql) throws SQLException {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:h2:mem:testdb", "sa", "");
Statement stat = conn.createStatement();
return stat.executeQuery(sql);
}
}
✅ 使用
@FixMethodOrder(NAME_ASCENDING)确保测试顺序,避免依赖混乱
6.2 测试步骤
(1) 初始状态:数据库为空
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenSessionInfoIsEmpty() throws SQLException {
assertEquals(0, getSessionIdsFromDatabase().size());
assertEquals(0, getSessionAttributeBytesFromDatabase().size());
}
(2) 访问首页:创建会话
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenOneSessionIsCreated() throws SQLException {
assertThat(this.testRestTemplate.getForObject(
"http://localhost:" + port + "/", String.class))
.isNotEmpty();
assertEquals(1, getSessionIdsFromDatabase().size());
}
✅ 首次请求触发会话创建,SPRING_SESSION 表中出现一条记录
(3) 提交颜色:验证属性持久化
@Test
public void whenH2DbIsQueried_thenSessionAttributeIsRetrieved() throws Exception {
MultiValueMap<String, String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
map.add("color", "red");
this.testRestTemplate.postForObject(
"http://localhost:" + port + "/saveColor", map, String.class);
List<byte[]> queryResponse = getSessionAttributeBytesFromDb();
assertEquals(1, queryResponse.size());
ObjectInput in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(queryResponse.get(0)));
List<String> obj = (List<String>) in.readObject();
assertEquals("red", obj.get(0));
}
⚠️ 注意:ATTRIBUTE_BYTES 存的是序列化后的对象,需要反序列化才能读取
7. 底层原理揭秘
看起来我们没做什么特别的事,但会话却自动存到了数据库。这背后的魔法在哪?
核心机制
当你配置 spring.session.store-type=jdbc 后,Spring Boot 实际上做了等价于以下操作:
@EnableJdbcHttpSession
这会自动注册一个名为 springSessionRepositoryFilter 的过滤器。
请求处理流程
- ✅ 每个 HTTP 请求被
springSessionRepositoryFilter拦截 - ✅ 原始
HttpServletRequest被包装成SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper - ✅ 调用
getSession()时,从数据库加载或创建新会话 - ✅ 请求结束时,自动调用
commitSession()将变更写回数据库
💡 你代码中用的还是标准
HttpSession,但背后已是数据库驱动的会话管理。
8. 查看数据库表结构
想亲眼看看会话数据长啥样?开启 H2 控制台即可。
启用 H2 Console
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
访问:http://localhost:8080/h2-console/
JDBC URL: jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
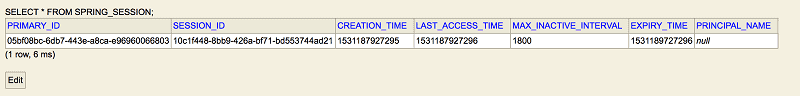
表结构截图
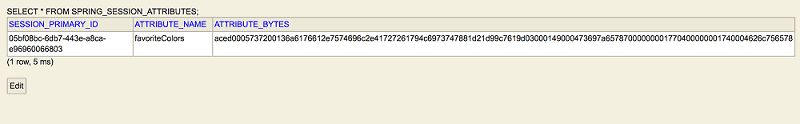
SPRING_SESSION_ATTRIBUTES 表:存储会话属性(序列化字节)
9. 总结
Spring Session + JDBC 是解决分布式会话问题的轻量级利器,尤其适合中小项目快速落地。
✅ 优势总结
- 零侵入:业务代码无需修改,仍用
HttpSession - 配置极简:Spring Boot 下仅需一行配置
- 支持多种数据库:H2、MySQL、PostgreSQL、Oracle 等
- 自动建表:提供标准 schema,开箱即用
- 扩展性强:可自定义序列化策略、表名、过期策略等
🚀 实际应用场景
- 多实例部署的 Web 应用
- 前后端分离项目中的会话保持
- 需要会话持久化的管理后台
🔗 想进一步了解 Spring Session 在安全认证中的应用?推荐阅读官方指南:Spring Session 完全指南
完整源码已托管至 GitHub:https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials/tree/master/spring-web-modules/spring-session