1. Overview
By default, LaTeX processes text in ASCII encoding, but modern publications sometimes require Unicode compatibility to handle a broader range of characters and languages.
In this tutorial, we’ll review how to compile LaTeX documents with UTF-8 encoding, a popular encoding supporting this larger character set.
2. Why Do We Need UTF-8 Encoding in LaTeX?
Setting up UTF-8 encoding in LaTeX allows us to manage various characters and ensure that all symbols appear in their correct forms:
Our goal isn’t just to produce output with such characters but also to use them directly in our document, i.e., in the source file.
3. PDFLaTeX
One of the most popular compilers for LaTeX documents with UTF-8 encoding is PDFLaTeX.
It creates a PDF file straight from the LaTeX source, which is useful for producing ready-to-print documents with excellent typesetting.
3.1. The inputenc Package
The inputenc package is required to specify how the compiler will read and interpret the characters in the input file.
To enable UTF-8 encoding, we must specify the utf8 option when including inputenc in our preamble:
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
Here, we tell LaTeX to read the document as UTF-8 encoded, which allows us to use characters other than the basic ASCII set.
For example, we can use various decorated characters, unusual symbols, or non-Latin scripts:
We can type such characters directly in the LaTeX document without using specific LaTeX commands. For instance, we can type ä and ß instead of \“a and \ss.
3.2. The fontenc Package
While inputenc allows LaTeX to decode UTF-8 characters from the source, the fontenc package controls how these characters appear in the output.
Additionally, without fontenc, LaTeX can fail to correctly render symbols, particularly for characters with accents, resulting in inconsistent font quality and various errors:
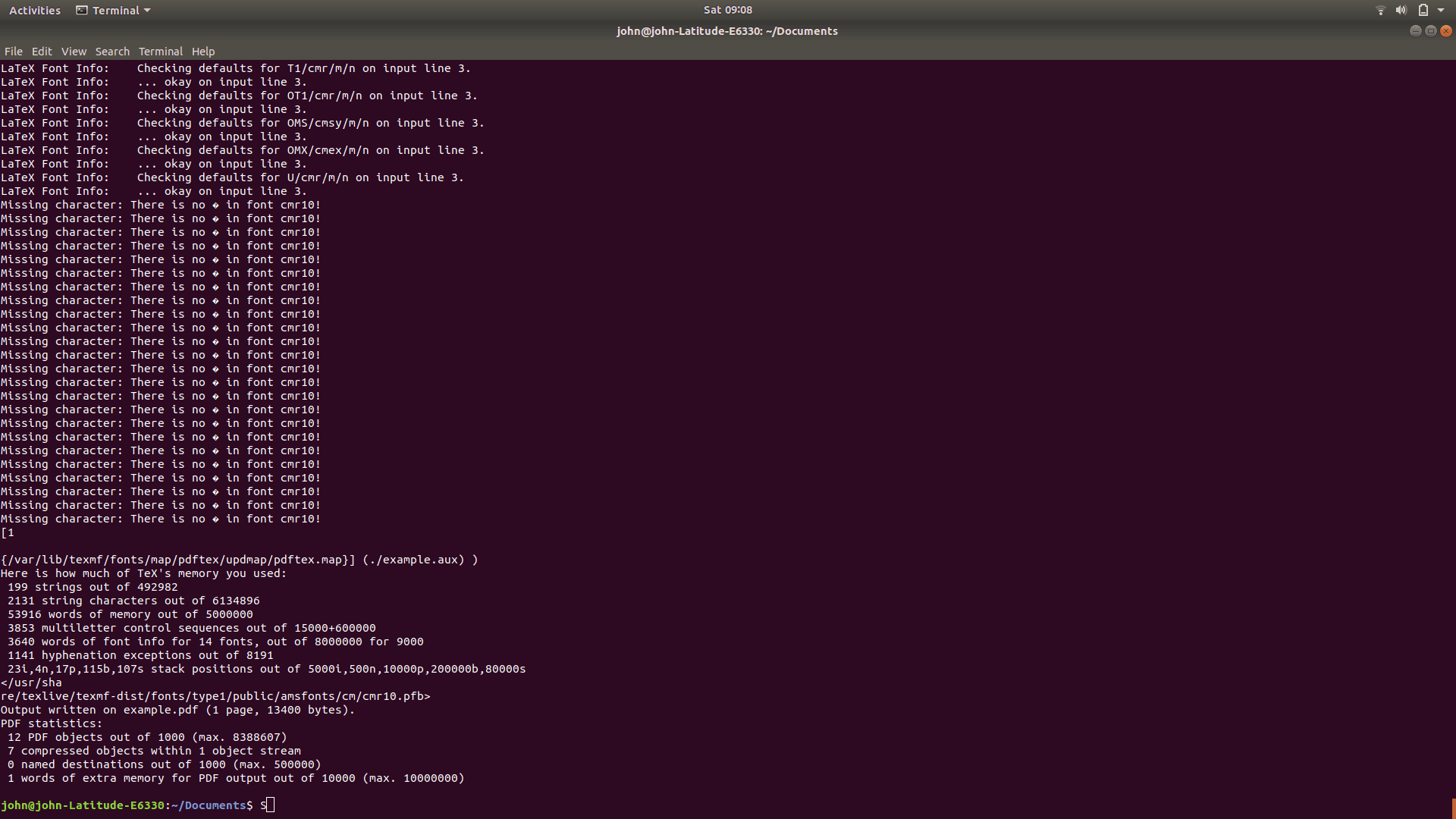
Specifying the T1 encoding with fontenc improves character handling in Western languages:
\usepackage[T1]{fontenc}
However, T1 doesn’t support all characters, so depending on what we need, we can consider other encodings, such as OT2 and T2A. For documents with Cyrillic characters, we use the T2A option to enable UTF-8.
In conclusion, fontenc complements inputenc by managing output rendering, whereas inputenc handles reading the input, i.e., our LaTeX document.
3.3. The babel Package
Depending on the language, we might have to add babel.
The babel package improves the ability of PDFLaTeX to process Latin and non-Latin scripts by adjusting hyphenation patterns, punctuation, and other settings to match the selected language.
For example, to select English as the language, we specify it as the option when importing babel:
\usepackage[english]{babel}
This line configures b**abel in our LaTeX document.
3.4. Basic Example
So, here’s our code snippet that produces the document with UTF-8 characters:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage[T2A]{fontenc}
\usepackage[english, russian]{babel}
\begin{document}
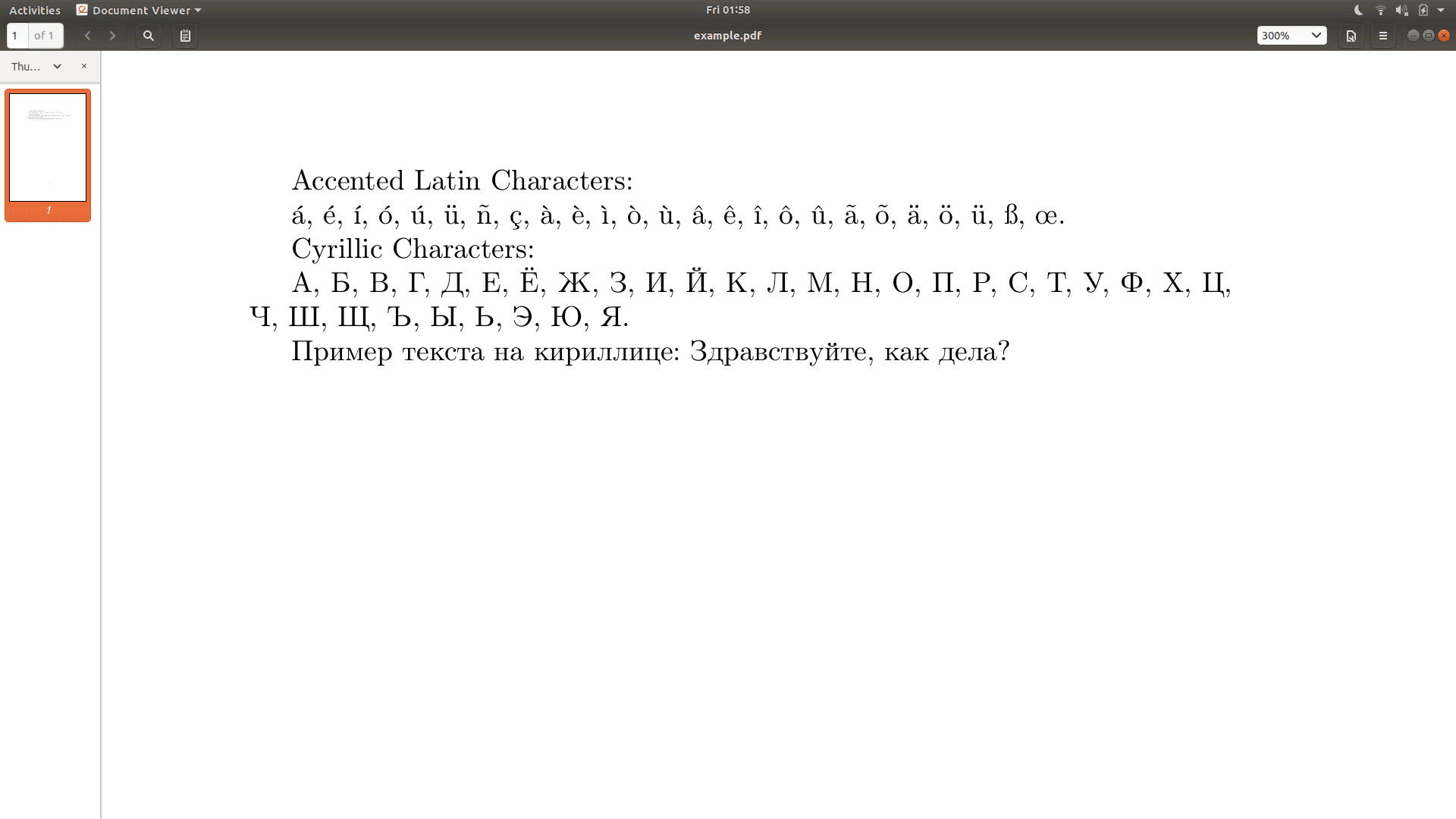
Accented Latin Characters:
á, é, ı́, ó, ú, ü, ñ, ç, à, è, ı̀, ò, ù, â, ê, ı̂, ô, û, ã, õ, ä, ö, ü, ß, œ.
Cyrillic Characters:
А, Б, В, Г, Д, Е, Ё, Ж, З, И, Й, К, Л, М, Н, О, П, Р, С, Т, У, Ф, Х, Ц, Ч, Ш, Щ, Ъ, Ы, Ь, Э, Ю, Я.
Пример текста на кириллице: Здравствуйте, как дела?
\end{document}
In this example, we used the babel package. Without babel, PDFLaTeX usually fails to correctly display Cyrillic characters.
To compile:
pdflatex file_name.tex
We use the pdflatex command to compile the .tex file and create a PDF with the same name, file_name.pdf, which contains all correctly rendered characters and symbols.
4. XeLaTeX and LuaLaTeX
XeLaTeX or LuaLaTeX offer native UTF-8 support for documents using a range of Unicode characters, such as Latin accents or non-Latin scripts, making it easier to include complex character sets.
4.1. The fontspec Package
We’ll use fontspec to configure UTF-8 encoding for Unicode fonts to manage language-specific grammar and formatting:
\usepackage{fontspec}
\setmainfont{DejaVu Serif}
In this example, we use the fontspec package to directly import Unicode-compliant system fonts. We opted for DejaVu Serif as the main font, but any font that supports UTF-8 can be selected using \setmainfont{Font Name}.
4.2. The polyglossia Package
The polyglossia package, an advanced alternative to babel, is used for multilingual documents. We can also use it to configure primary and secondary languages:
\usepackage{polyglossia}
\setmainlanguage{english}
\setotherlanguage{russian}
In this example, we included polyglossia and set English as the primary language \setmainlanguage{english} and Russian \setotherlanguage{russian} as an optional language to show Russian Cyrillic characters correctly. Other Cyrillic scripts, such as Serbian or Bulgarian, will require to set Serbian or Bulgarian as the language. Similar holds for other scripts.
4.3. Basic Example
So, here’s our code snippet that produces the document with UTF-8 characters:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{fontspec}
\usepackage[english, russian]{babel}
\setmainfont{DejaVu Serif}
\begin{document}
Accented Latin Characters:
á, é, ı́, ó, ú, ü, ñ, ç, à, è, ı̀, ò, ù, â, ê, ı̂, ô, û, ã, õ, ä, ö, ü, ß, œ.
Cyrillic Characters:
А, Б, В, Г, Д, Е, Ё, Ж, З, И, Й, К, Л, М, Н, О, П, Р, С, Т, У, Ф, Х, Ц, Ч, Ш, Щ, Ъ, Ы, Ь, Э, Ю, Я.
Пример текста на кириллице: Здравствуйте, как дела?
\end{document}
To compile with XeLaTeX:
$ xelatex file_name.tex
To compile with LuaLaTeX:
$ lualatex file_name.tex
We use the xelatex or lualatex command to compile the .tex file and create a PDF with the same name, file_name.pdf, which contains all correctly rendered characters and symbols.
4. Conclusion
In this article, we discussed how to compile a LaTeX document using UTF-8 encoding. This is required for dealing with various languages, symbols, and characters in modern typesetting.
While PDFLaTeX works well for many UTF-8 documents, XeLaTeX and LuaLaTeX provide better Unicode compatibility and simple integration with system fonts, making them great for multilingual projects.