1. Overview
Nowadays, generative AI tools are everywhere, helping users create text, videos, images, summaries, and more in an instant. Yet, we struggle to achieve the exceptional quality that experts produce with these tools. Why? The answer is simple, we don’t provide high-quality input, known as a prompt, to produce accurate, exceptional outputs.
In this tutorial, we’ll learn about prompt engineering and its importance. Also, we’ll learn about various prompt techniques and components.
2. What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is a technique that involves providing a descriptive and meaningful prompt in natural language to generative AI tools to obtain an optimal and efficient result as per expectations. It’s crucial to craft a prompt that’s not vague and clearly depicts the requirement in a concise way to properly describe what we require.
It’s safe to say that the relationship between a prompt and the output of a generative AI is directly proportional. Thus, we’ll get accurate output only if the input prompt is engineered optimally.
3. Why Prompt Engineering Is Important
The more descriptive and well-communicated the prompt is, the more accurate the results will be. In addition to producing desired outputs, the prompt engineering technique is also used by AI engineers to train LLMs (Large Language Models).
3.1. Improving AI Performance with Effective Prompts
As we’ve mentioned earlier, effective prompts improve the performance of AI tools. Let’s take a basic example to illustrate this point.
For instance, if we want an image of a specific breed of kitten on a specific tree, we can’t simply provide a prompt saying a cat on a tree, it’ll not produce the desired results. Instead, we’re required to provide a more descriptive prompt, such as the one below:
A realistic 4-week-old British Shorthair kitten sitting on a delicate cherry blossom tree branch, with soft rays of sunlight filtering through the leaves, casting a warm glow on the branch and kitten. The background features a serene spring sky, with pink cherry blossoms in full bloom surrounding the kitten.
This prompt interprets our needs in words. Let’s see the image that showcases the difference in results between both prompts:
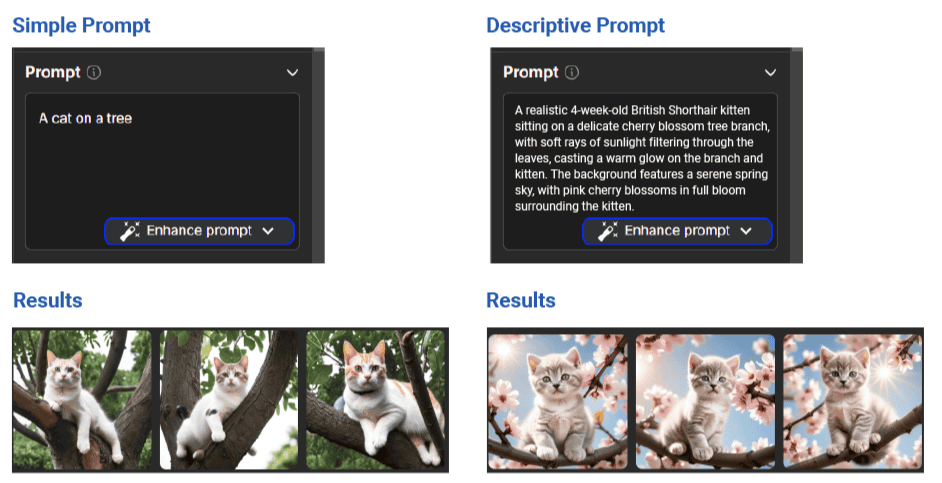
The above images were created using the free version of DALL·E. We can further enhance the prompt by utilizing the DALL·E’s prompt book.
3.2. Rising Demand for Prompt Engineers
Many software companies are looking for skilled prompt engineers to join their data science teams to design and generate prompts for various applications. Let’s list some of the key skills a prompt engineer must have:
- Knowledge of AI, NLP, machine learning, and neural networks
- Proficiency in programming languages, such as Python
- Excellent problem-solving and analytical skills
- Experience with AI frameworks
Currently, an intermediate-level prompt engineer typically earns between $110,000 and $130,000 per annum. Interestingly, it’s still one of the jobs whose demand is rapidly increasing as AI continues to grow.
4. Components of Prompts
Moving onward, let’s now learn about the components that enable users to develop a great prompt. These components are task, context, example, role, format, and tone. The image below showcases the order of importance we need to consider when crafting a prompt:
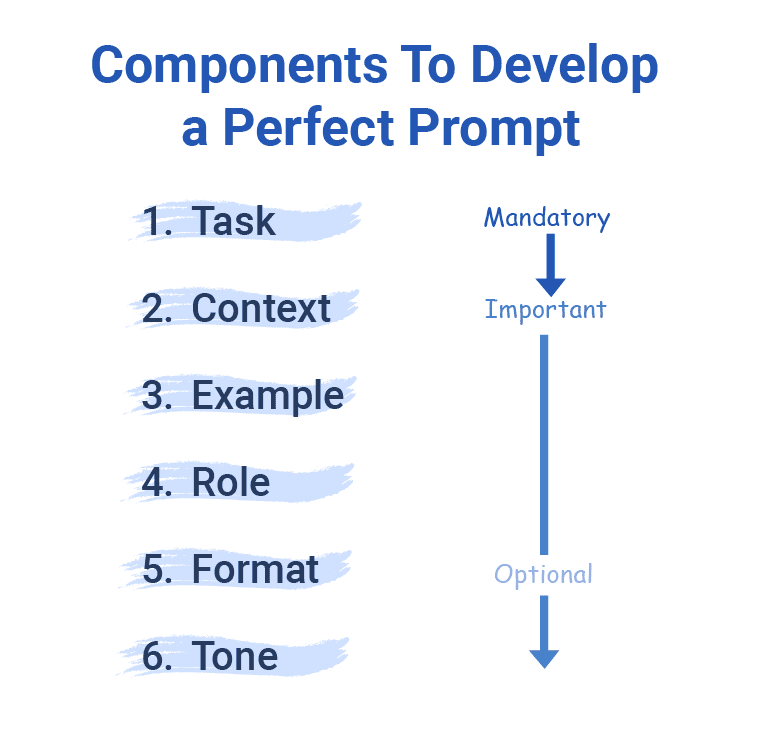
4.1. Task and Context
Indeed, we’re required to provide a task to the generative model to get an output. Notably, we’re required to include action verbs in the task, such as write and design. However, if we provide context before the task, we can craft a better prompt. The context provides extra information, such as background, ideal conditions, or success metrics.
For instance, instead of simply asking to write an email for a leave application, we can give context explaining why we require time off and then state the clear task, such aswritinge a brief leave email.
4.2. Example
In addition to context and task, we can also include relevant examples to make the prompt more accurate and descriptive. For instance, we can provide an example of a well-formatted leave email to guide the AI tool in formatting the response. However, it’s not always necessary to provide examples in the prompt.
4.3. Role
Besides examples, we can also assign a role to the generative AI tool. For instance, we can ask ChatGPT to act as an interviewer and ask questions for a software engineer job based on the resume and job description provided, along with answers for securing the job. This way, we’ll get quality questions and answers for interview preparation.
4.4. Format and Tone
Moreover, we can specify the format for the output, such as asking for a table, list, or code block, or requesting that main points be italicized. For example, we can specify that each interview answer should be under 300 characters and formatted in a table with column headers like Questions, Answers, and Tips.
Lastly, we can specify the tone of the result, such as casual, professional, confident, etc.
Now, we can use all or a combination of some of these components to develop a perfect prompt that generates a useful, accurate response.
5. Prompt Engineering Techniques
Besides the components of prompts, we also have various techniques for providing prompts to generative AI tools. Let’s discuss some of the common techniques briefly:
Technique
Description
Zero-Shot Prompting
This technique refers to the practice of asking a generative AI tool to perform a task without providing any prior examples. Overall, this is ideal when users require quick, straightforward results for well-defined tasks.
Few-Shot Prompting
In the few-shot prompting technique, we provide a few examples in the prompt to help the AI understand the task better. These examples serve as context, improving the model’s accuracy and output. Overall, it works best when we require responses for complex tasks.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
This technique breaks down a task into smaller steps, guiding the generative AI tool through a logical progression. It helps the tool tackle complex questions with step-by-step reasoning. Overall, we use it when solving multi-step problems or generating structured outputs.
Prompt Chaining
The prompt chaining technique connects multiple prompts in a sequence, where each step builds on the output of the previous one. It helps the AI handle larger tasks in smaller, manageable pieces. Overall, it’s ideal for workflows that require a series of actions or interconnected results.
Tree of Thoughts
This technique uses a branching approach to represent various possible paths and solutions to a problem. Overall, it’s ideal for scenarios where we require the generative AI tool to evaluate multiple possibilities before making a decision.
Multimodal CoT
This technique combines multiple forms of input, like text and images, into the reasoning process. Overall, it’s ideal for situations when we require the AI to handle tasks that involve multiple types of information, such as images and text.
The above table discussed some of the common prompt techniques. Consequently, we can experiment with combinations of these techniques and prompt components to obtain the desired results.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we discussed that prompt engineering is a process of communicating with generative AI tools to obtain accurate results. Nowadays, with the rapid growth in the AI sector, the demand for prompt engineers is increasing, as it’s crucial for training LLMs. However, even if we’re not prompt engineers, we can use various prompt components and techniques to get optimal results for our personal and professional use.