1. 介绍
本文将带你快速了解 JanusGraph 和 Gremlin。
JanusGraph 是一个开源、支持大规模扩展的图数据库。它专为处理超大规模图而设计——大到需要多个数据库节点协同工作——同时仍保持高效的查询性能。
✅ 核心优势:
- 基于成熟技术栈构建(如 Cassandra、HBase、Elasticsearch)
- 原生集成 Apache TinkerPop 生态
- 支持 Gremlin 控制台和查询语言
⚠️ 适合场景:需要处理复杂关系数据(如社交网络、知识图谱)且要求高扩展性的项目。
2. 运行 JanusGraph 和 Gremlin
本地运行需要下载最新版本(当前版本 1.1.0),解压后确保已安装 Java 8+ JVM。
在解压目录执行以下命令启动 Gremlin 会话:
-> % ./bin/gremlin.sh
\,,,/
(o o)
-----oOOo-(3)-oOOo-----
plugin activated: tinkerpop.server
plugin activated: tinkerpop.tinkergraph
08:45:56 INFO org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.jsr223.HadoopGremlinPlugin.getCustomizers - HADOOP_GREMLIN_LIBS is set to: /Users/baeldung/janusgraph-1.1.0/lib
08:45:56 WARN org.apache.hadoop.util.NativeCodeLoader.<clinit> - Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
plugin activated: tinkerpop.hadoop
plugin activated: tinkerpop.spark
plugin activated: tinkerpop.utilities
plugin activated: janusgraph.imports
这个 Gremlin 实例可直接托管 JanusGraph 数据库,特别适合快速测试。通过 JanusGraphFactory.open 指定配置文件:
gremlin> graph = JanusGraphFactory.open('conf/janusgraph-inmemory.properties')
08:46:06 INFO org.apache.commons.beanutils.FluentPropertyBeanIntrospector.introspect - Error when creating PropertyDescriptor for public final void org.apache.commons.configuration2.AbstractConfiguration.setProperty(java.lang.String,java.lang.Object)! Ignoring this property.
08:46:06 INFO org.janusgraph.diskstorage.configuration.builder.ReadConfigurationBuilder.setupTimestampProvider - Set default timestamp provider MICRO
08:46:06 INFO org.janusgraph.graphdb.idmanagement.UniqueInstanceIdRetriever.getOrGenerateUniqueInstanceId - Generated unique-instance-id=c0a801777851
08:46:06 INFO org.janusgraph.diskstorage.configuration.ExecutorServiceBuilder.buildFixedExecutorService - Initiated fixed thread pool of size 16
08:46:06 INFO org.janusgraph.graphdb.database.StandardJanusGraph.<init> - Gremlin script evaluation is disabled
08:46:06 INFO org.janusgraph.diskstorage.log.kcvs.KCVSLog$MessagePuller.initializeTimepoint - Loaded unidentified ReadMarker start time 2025-02-24T08:46:06.291970Z into org.janusgraph.diskstorage.log.kcvs.KCVSLog$MessagePuller@21eedcde
==>standardjanusgraph[inmemory:[127.0.0.1]]
这会创建一个 graph 变量作为后续操作的入口。配置文件 janusgraph-inmemory.properties 使用纯内存存储(无持久化),是最简单的配置。
2.1. 独立服务器模式
也可通过 ./bin/janusgraph-server.sh start 启动独立服务器:
-> % ./bin/janusgraph-server.sh start
/Users/baeldung/janusgraph-1.1.0/conf/gremlin-server/gremlin-server.yaml will be used to start JanusGraph Server in background
Server started 8163
默认监听 8182 端口,使用相同的内存配置。此时可通过远程客户端连接:
gremlin> :remote connect tinkerpop.server conf/remote.yaml session
08:54:19 INFO org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.Connection.<init> - Created new connection for ws://localhost:8182/gremlin
08:54:19 INFO org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ConnectionPool.<init> - Opening connection pool on Host{address=localhost/127.0.0.1:8182, hostUri=ws://localhost:8182/gremlin} with core size of 1
==>Configured localhost/127.0.0.1:8182-[96b90c45-4aef-405d-a336-5823bcde3995]
启用远程模式后,所有命令将发送到服务器:
gremlin> :remote console
==>All scripts will now be sent to Gremlin Server - [localhost/127.0.0.1:8182]-[96b90c45-4aef-405d-a336-5823bcde3995] - type ':remote console' to return to local mode
❌ 注意:远程模式下无需手动创建 graph 变量,服务器会自动配置。
3. 图结构
JanusGraph 使用图模型存储数据,核心元素是:
- 顶点(Vertex):实体节点
- 边(Edge):连接顶点的有向关系
✅ 关键特性:
- 边必须连接两个顶点且有方向(有向图)
- 允许存在任意长度的环(非无环图)
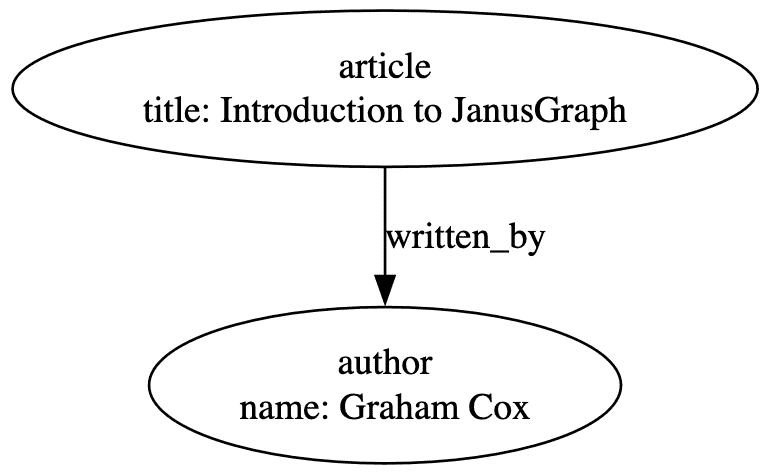
- 数据通过标签(Label)和属性(Property)表示:
- 边必须有标签(如
written_by) - 顶点可选标签(如
article) - 支持任意键值对属性(如
title: "Introduction to JanusGraph")
- 边必须有标签(如
⚠️ 踩坑提示:设计标签体系时需提前规划,频繁修改标签类型可能导致性能问题。
4. 加载示例数据
Gremlin CLI 内置示例数据加载工厂:
gremlin> GraphOfTheGodsFactory.loadWithoutMixedIndex(graph, true)
==>null
这会加载名为"众神之图"(The Graph Of The Gods)的罗马神话数据集:
该数据集包含:
- 神祇(如木星、冥王)
- 半神(如赫拉克勒斯)
- 怪物(如地狱犬、九头蛇)
- 地点和战斗关系
足够演示 JanusGraph 的核心操作。
5. 查询数据
创建遍历源(Traversal Source)是查询的第一步:
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[standardjanusgraph[inmemory:[127.0.0.1]], standard]
g 变量作为后续遍历操作的入口。
5.1. 查询顶点
列出所有顶点(简单粗暴但效率低):
gremlin> g.V()
08:13:56 WARN org.janusgraph.graphdb.transaction.StandardJanusGraphTx$3.execute - Query requires iterating over all vertices [[]]. For better performance, use indexes
==>v[4136]
==>v[8232]
==>v[12328]
==>v[4184]
==>v[8280]
==>v[4216]
==>v[8312]
==>v[12408]
==>v[4256]
==>v[4288]
==>v[8384]
==>v[4304]
⚠️ 警告:全表扫描性能差,生产环境务必使用索引。
按属性过滤顶点:
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules')
==>v[4136]
获取顶点详情:
# 返回所有属性
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').valueMap()
==>[name:[hercules],age:[30]]
# 获取标签
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').label()
==>demigod
# 获取单个属性值
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').values('name')
==>hercules
保存结果到变量:
gremlin> hercules = g.V().has('name', 'hercules').next()
==>v[4128]
后续可通过变量引用:
gremlin> g.V(hercules).valueMap()
==>[name:[hercules],age:[30]]
5.2. 遍历边
边遍历是图数据库的核心优势。使用 in() 和 out() 按方向遍历:
向外遍历(从当前顶点出发的边):
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').out('father').valueMap()
==>[name:[jupiter],age:[5000]]
向内遍历(指向当前顶点的边):
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'jupiter').in('father').valueMap()
==>[name:[hercules],age:[30]]
处理多结果集:
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').out('battled').valueMap()
==>[name:[cerberus]]
==>[name:[hydra]]
==>[name:[nemean]]
链式过滤:
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').out('battled').has('name', 'hydra').valueMap()
==>[name:[hydra]]
复杂多跳遍历(找出与赫拉克勒斯战斗的怪物所在地的其他居民):
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'hercules').out('battled').out('lives').in('lives').valueMap()
==>[name:[cerberus]]
==>[name:[pluto],age:[4000]]
执行逻辑:
- 找到
name="hercules"的顶点 - 遍历所有
battled边到达怪物顶点 - 从怪物顶点遍历
lives边到达地点 - 从地点顶点反向遍历
lives边找到所有居民
6. 添加和编辑数据
添加新顶点:
gremlin> theseus = graph.addVertex('human')
==>v[16552]
添加带属性的顶点:
gremlin> theseus = graph.addVertex(T.label, 'human', 'name', 'theseus')
==>v[12528]
❗ 注意:标签使用特殊键 T.label 指定。
更新顶点属性:
gremlin> theseus.property('name', 'theseus')
==>vp[name->theseus]
创建边:
gremlin> cerberus = g.V().has('name', 'cerberus').next()
==>v[12496]
gremlin> theseus.addEdge('met', cerberus)
08:00:36 INFO org.janusgraph.graphdb.relations.RelationIdentifier.<clinit> - Use default relation delimiter: -
==>e[3z2-9o0-hed-9n4][12528-met->12496]
验证新数据:
gremlin> g.V().has('name', 'theseus').out('met').valueMap()
==>[name:[cerberus]]
7. 总结
本文快速介绍了 JanusGraph 的核心功能,包括:
- 本地/服务器模式部署
- 图数据模型设计
- 示例数据加载
- Gremlin 查询与遍历
- 动态数据操作
这只是 JanusGraph 能力的冰山一角。当你下次需要处理复杂关系数据时,不妨试试这个强大的图数据库——它可能正是你需要的"关系挖掘利器"。